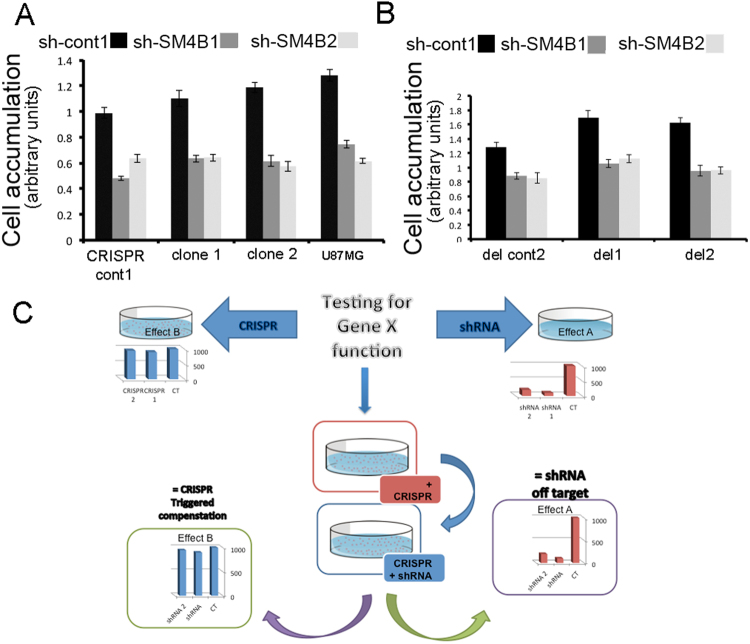
Figure 6.
Combined shRNA over CRISPR/cas9 as a methodology to detect off targets and potential compensatory mechanism. (A–C) shRNA over CRISPR/cas9 cell lines. (A,B) Resazurin cell viability assay was used to evaluate cell number. CRISPR-cas9 clone 1 and 2 (mutations in signal sequence of Sema4B) and cont line 1 (A) or clones in which the genomic locus was deleted (B), del1, del2 and del-cont 2,) were subdivided each into three groups. Each group was infected with shRNA targeting Sema4B (sh-SM4B1, sh-SM4B2) or control (sh-cont). Note that in all four lines, whether or not they express Sema4B, proliferation was reduced by shRNA targeting Sema4B, thus demonstrating that the effects on proliferation are the result of an off target effect. Data in (A) and (B) represents the means of n = 3 independent repetitions ± s.e.m. (C) Flow chart demonstrating the steps in the methodology to differentiate between off target effects and compensatory mechanism. (1) To test the role of a gene X in a specific function we propose to compare the results of shRNA (or siRNA) with the effects of CRISPR-Cas9 targeting the same gene X. In cases in which shRNA has an effect while CRISPR-Cas9 does not, we propose to first mutate gene X using the CRISPR-Cas9 method, followed by shRNA to the same gene. There are two possible outcomes: (1) a result similar to the effects of shRNA = an off target effect; (2) a result similar to the effects of CRISPR-Cas9 = result represents a compensation mechanism triggered by the genetic mutation.