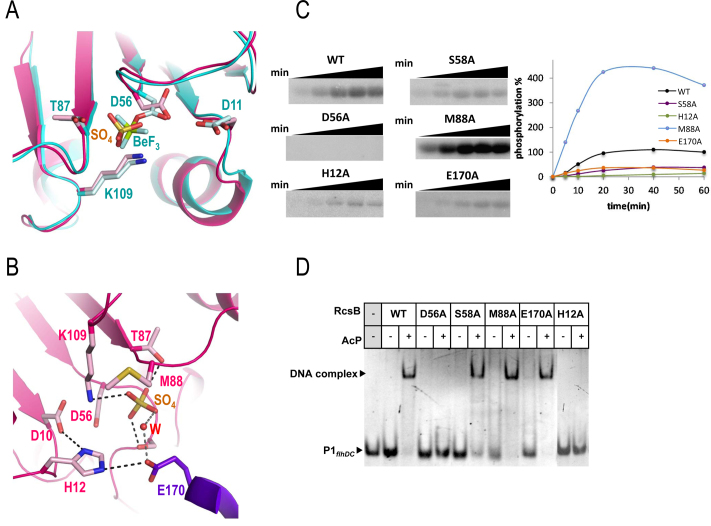
Figure 4.
Active site and functional studies on catalytic residues in RcsB. (A) Detail of the active site for RcsBcrossed (in pink) superposed with RcsBBeF (in cyan). Catalytic residues as well as the sulfate ion (SO42− labeled as SO4) and BeF3−(labeled as BeF) are shown as sticks. (B) Another view of the active site in RcsBcrossed (pink for one subunit and purple for the other). Residue E170 (in purple) from the DBD of the other subunit contributes to the active site. Catalytic and relevant residues are shown as sticks together with the sulfate ion (SO4) and a water molecule (W). (C) Phosphorylation assays of WT and mutants of RcsB with AcP32. Phosphorylation was followed at 5, 10, 20, 40 and 60 min and was evaluated with the MultiGauge software (Fuji). (D) EMSAs of RcsB WT and mutant forms with P1flhDC were performed in the absence and presence of 50 mM of AcP.