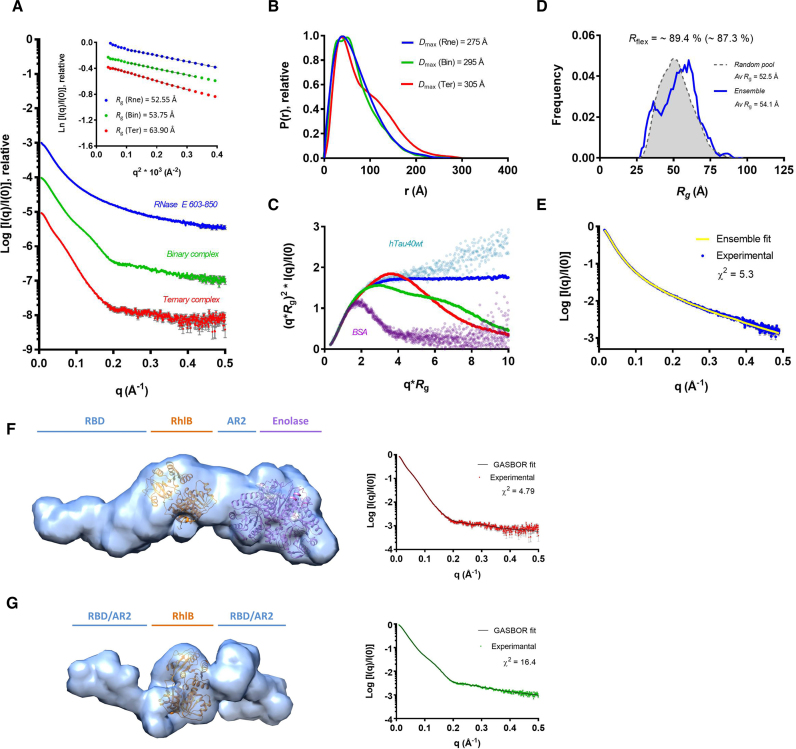
Figure 3.
SAXS analysis of degradosome subassemblies; RNase E 603–850/RhlB/enolase ternary complex (Ter, red), RNase E 603–850/RhlB binary complex (Bin, green) and RNase E 603–850 (Rne, blue). (A) Scattering intensity profiles with inset Guinier regions incorporating fits and derived Rg values. (B) P(r) distribution functions, with respective Dmax values. (C) Dimensionless Kratky plot overlay of the ternary complex, binary complex and RNase E 603–850 compared to references; the globular BSA and highly flexible hTau40wt proteins (66) (D) Flexibility assessment of RNase E 603–850: the Rg distribution for the random pool of models (gray) and for the ensemble of conformations that altogether give a good fit to the scattering intensity curve (blue) are shown, with Rflex values of 87.3 and 89.4%, respectively. (E) RNase E 603–850 experimental scattering intensity curve (blue) with ensemble model fit (yellow line). (F and G) Ab initio reconstruction of the degradosome recognition core. Molecular envelopes of (F) the RNase E 603–850/RhlB/enolase ternary complex and (G) RNase E 603–850/RhlB binary complex, calculated in GASBOR. A homology model of RhlB, generated in Phyre2 program (67) based on the crystal structure of the Drosophila DEAD box helicase VASA (51), in addition to the crystal structure of enolase (PDB: 3H8A; 52) were docked into the shapes using the automatic function in the program Chimera (44). The space flanking RhlB corresponds to the RBD and AR2, for which there are no experimentally determined structural models. The X-ray scattering intensity profile of the ternary complex (red) and binary complex (green) overlaid on respective theoretical curves from ab initio models (black line) are shown to the right of the respective models. Visually the experimental scattering intensities have an excellent fit to the model scattering intensity curves, although χ2 values are relatively high (4.8 and 16.4, respectively) due to high signal-to-noise ratio.