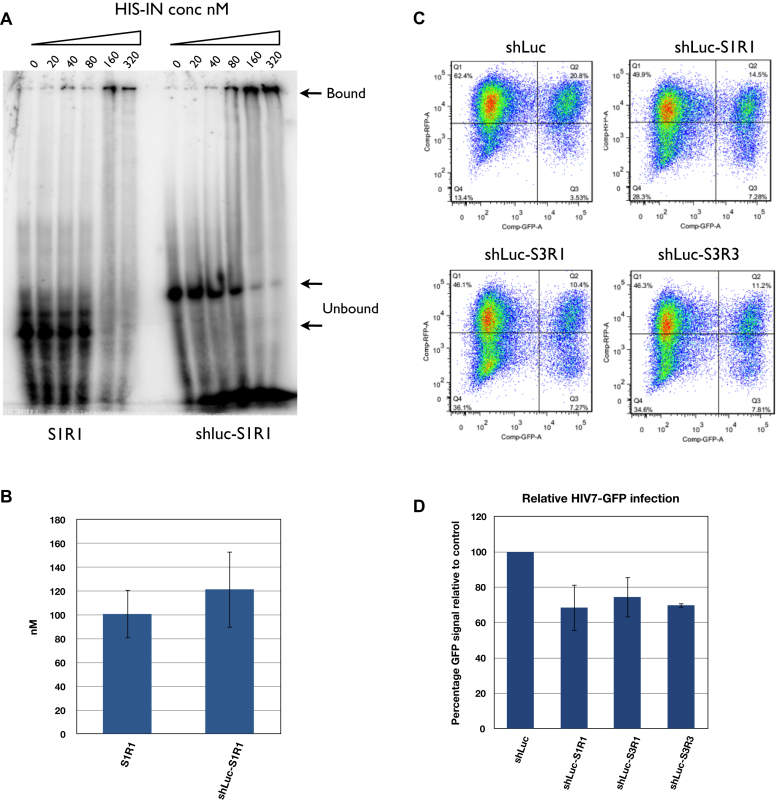
Figure 5.
shLuc-aptamer fusion showed weaker binding to HIS-IN but stronger inhibition of lentivirus infection than aptamer alone. (A) Mobility shift assay comparing aptamer S1R1 alone and shLuc-S1R1 fusion. Unbound aptamers were indicated by lower arrows (59 nucleotides long for S1R1 and 96 nucleotides long for shLuc-S1R1). Bound aptamers appeared to form very large complexes with IN and retained in the wells (upper arrow). Signals from lower bands were used to calculate the 50% binding value. (B) Quantification of affinity of S1R1 and shLuc-S1R1 to HIS-IN. Concentrations at which 50% of probe shift were shown. Binding of S1R1 was the average of three independent assays while that of shLuc-S1R1 was the average of two independent assays. (C) FACS analysis of HEK293 cells expressing shLuc alone or shLuc-aptamer fusions infected by HIV7-GFP lentivirus at MOI of 0.3. (D) Quantification of FACS analysis. Percentage of double-positive (Q2) over total GFP-positive (Q2+Q3) was compared to shLuc control (100%). Averages and standard deviations of three independent assays are shown.