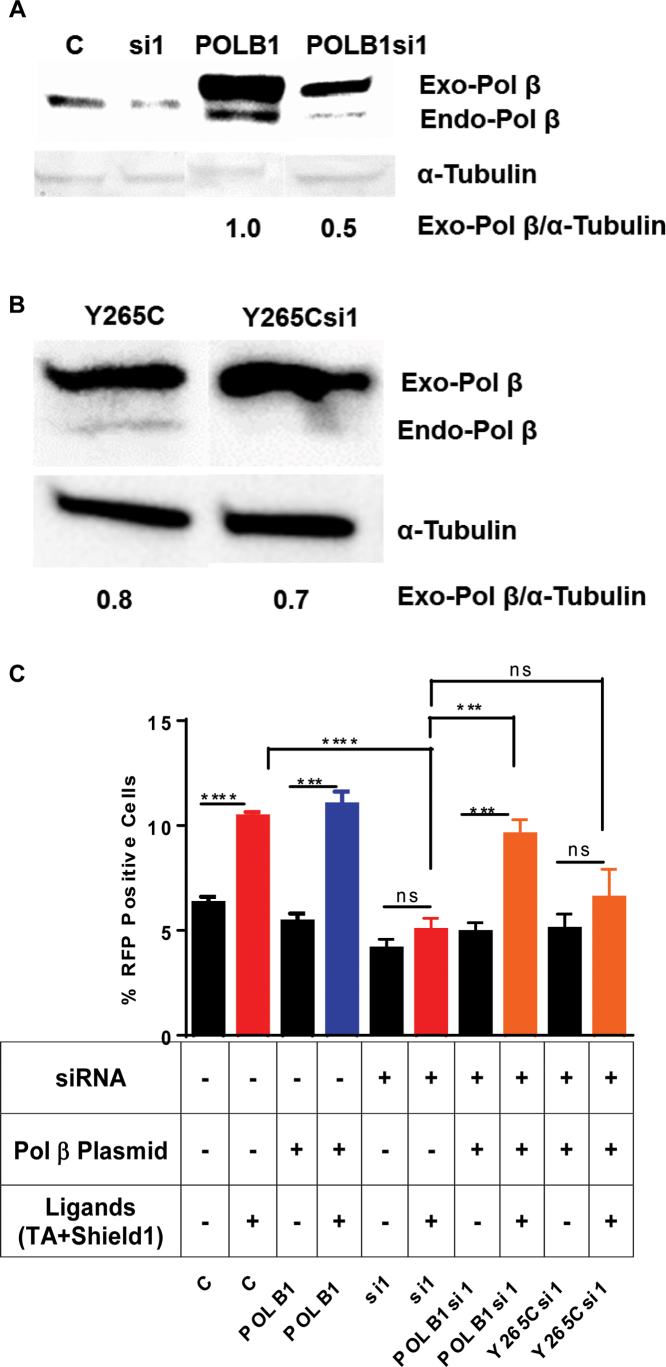
Figure 2.
Overexpression of Pol β rescues the deficiency of mutagenic end-joining in Pol β-depleted cells. (A) Western blot. Exogenous-Pol β (Exo-Pol β) is exogenously expressed Pol β from the siRNA-resistant plasmid harboring the POLB cDNA and endogenous-Pol β (Endo-Pol β) is endogenously expressed protein. C denotes negative non-targeting siRNA control; si1 denotes cells treated with si1 targeted against the POLB gene; POLB1 denotes overexpression of Pol β protein in cells by treating them with a plasmid harboring the cDNA of the POLB gene that is resistant to si1; POLBsi1 denotes cells treated with both siRNA1 targeting the POLB gene and a plasmid overexpressing Pol β. The exogenously expressed protein carries an HA epitope tag, resulting in its slower resolution, versus endogenous protein, in the gel. Quantification at the bottom of the image Exo-Pol β/tubulin. (B) Exogenous-Y265C-Pol β (Exo-Pol β-Y265C) is exogenously expressed Pol β from the siRNA-resistant plasmid harboring the Y265C POLB cDNA and endogenous-Pol β (Endo- Pol β) is endogenously expressed protein. Y265C denotes overexpression of Y265C-Pol β protein in cells by treating them with a plasmid harboring the cDNA of the Y265C POLB gene that is resistant to si1; Y265Csi1 denotes cells treated with both siRNA1 targeting theY265C POLB gene and a plasmid overexpressing Y265C-Pol β. The exogenously expressed protein carries an HA epitope tag, resulting in it's slower resolution, versus endogenous protein, in the gel. (C) Overexpression of Pol β rescues the aNHEJ deficiency in cells treated with siRNA targeting the POLB gene. But the overexpression of Y265C-Pol β does not rescue the aNHEJ deficiency. The percentage of RFP+ cells plotted on the Y-axis. Data are graphed as mean ± SEM (n = 3) **** (P < 0.0001) *** (P = 0.0009) and P = ns (not significant).