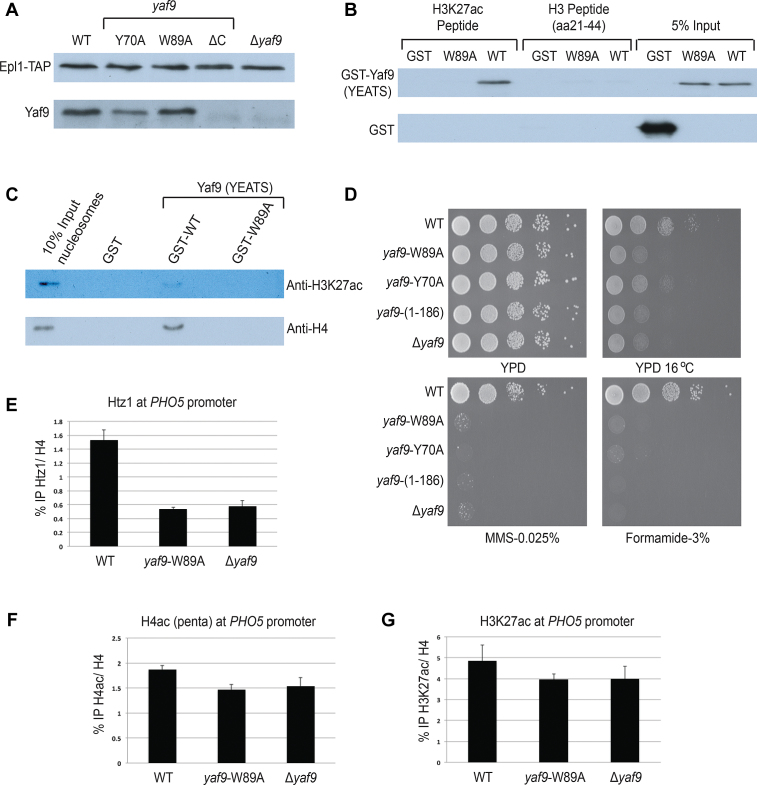
Figure 3.
Mutations in Yaf9-YEATS disrupt binding to H3K27ac in vitro and loading of H2A.Z in vivo. (A) TAP purification of NuA4 complex using Epl1-TAP tagged background. Yaf9 WT and point mutants (Y70A and W89A) associate with the NuA4 complex, but the C-terminal truncated form (ΔC; 1–186 aa) of Yaf9 does not. Purified NuA4 complex was ran on 10% Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane and detected with indicated antibodies. (B) Peptide pull-down assay using indicated H3 peptides and GST-tagged Yaf9-YEATS. Recombinant WT Yaf9 binds to H3K27ac peptides, whereas the W89A mutant does not. None of the proteins show binding to unmodified H3 peptide. Empty GST is used as negative control. (C) Chromatin pull-down assay using human nucleosomes and GST-tagged Yaf9-YEATS. WT Yaf9 binds to nucleosomes harboring the H3K27ac mark, while the W89A mutant does not. Empty GST is used as negative control. (D) Phenotypic analysis of yeast strains with integrated alleles YAF9 (WT), yaf9-Y70A, yaf9-W89A, yaf9(1–186) and Δyaf9. The strains expressing the YEATS domain point mutants showed similar growth defects as truncated yaf9(1–186) and Δyaf9 at 16°C, and in the presence of formamide or DNA-damaging agent MMS. (E) The point mutation W89A introduced in endogenous Yaf9 creates a strong defect in incorporation of histone variant H2A.Z (Htz1) at the PHO5 gene promoter in vivo. ChIP-qPCR was performed using anti-Htz1 and anti-H4 antibodies and the indicated yeast strains. The precipitated DNA was quantified with primers spanning the PHO5 UAS2 region. Data are presented as ratio of IP for Htz1 normalized on total H4. The error bar represents range between two biological replicates. (F and G) Levels of H4 hyperacetylation and H3K27ac were measured by ChIP-qPCR in the same conditions as in (E).