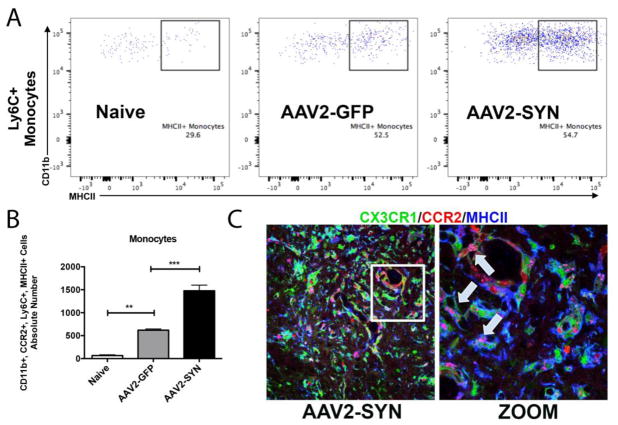
Figure 4. CCR2-RFP+ peripheral monocytes are pro-inflammatory via MHCII expression.
(A) CD45+, CD11b+, myeloid cell populations were gated to isolate CX3CR1-GFPlo, CCR2-RFP+ infiltrating myeloid cells. Further gating on Ly6C and M1 marker, MHCII showed and increase in the absolute number of CCR2-RFP+, Ly6C+, MHCII+ infiltrating monocytes in AAV2-SYN injected red/green mice when compared to Naïve and AAV2-GFP controls (B). Quantification of the absolute number of MHCII+, Ly6C+ monocytes in the ventral midbrain of Naïve, AAV2-GFP, and AAV2-SYN transduced red/green mice. This experiment involves 28 mice. Individual samples were formed by pooling 2 ventral midbrains, each from different animals (bilaterally injected). In each experiment, treatment groups (Naïve, AAV2-GFP, AAV2-SYN) consisted of 4 of these independent samples. For flow cytometry analysis, the mean +/− SEM of the independent samples in each treatment group were plotted. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (C) CCR2-RFP+ infiltrating cells (red) co-localize with MHCII I-A/I-E proteins (blue, arrow inset) in the AAV2-SYN transduced SNpc of red/green mice at 4 weeks. GFP is CX3CR1.