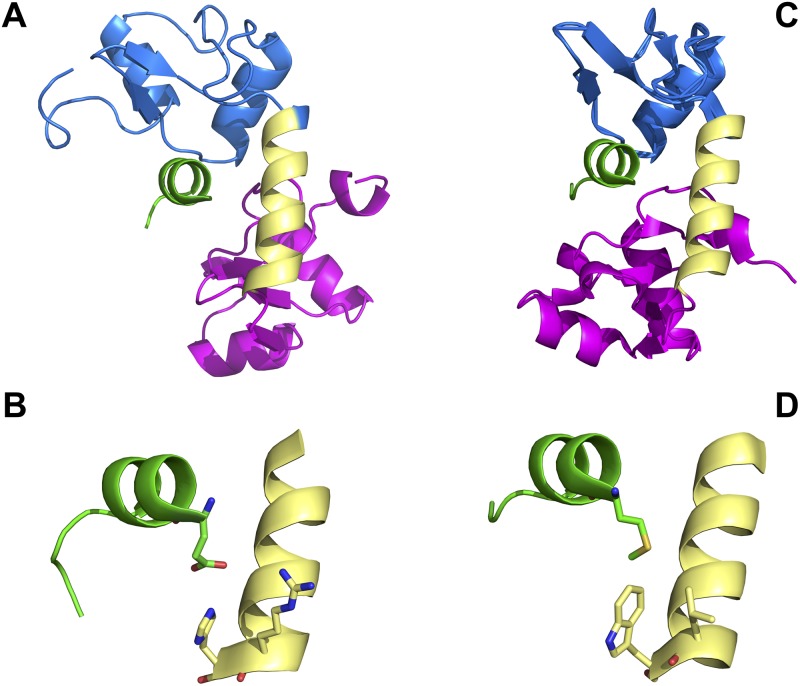
Fig 2. Contact residues in HPV16 E6 and BPV1 E6 that distinguish between E6AP interaction and MAML1 interaction.
A. HPV16 E6 structure (PDB file 4GIZ [41]) showing the amino-terminal zinc structured domain in blue, the connecting helix in yellow and the carboxy-terminal zinc-structured domain in pink) in association with the LXXLL peptide of E6AP (green) where the amino-terminal position -3 is facing the viewer. B. A close-up detail from part A of the HPV16 E6 –E6AP structure showing the interaction between position -3 of the E6AP LXXLL peptide (glutamic acid) with 16E6 amino acids R77 and H78. C. The structure of BPV1 E6 in association with the LXXLL peptide of paxillin (PDB file 3PY7 [41]) in similar orientation to the structure in part A. D. A close-up detail from part C of the BPV1 E6 structure showing the interaction between position -3 of the PXN LXXLL peptide (methionine) with BPV1 E6 amino acids L64 and W65.