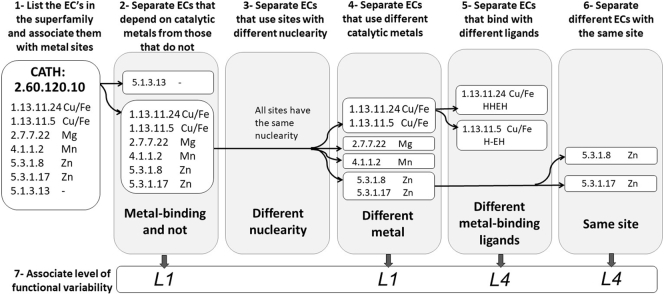
Fig. 1.
Pipeline to separate a given CATH superfamily into defined subgroups based on subsequent splitting events. The occurrence of splitting events (steps 1–6) is evaluated hierarchically. The level of functional differentiation (defined as the highest level at which the EC numbers changed for any possible pair of superfamily members in the different subgroups created) is assigned to each splitting event at the end of the procedure (step 7). It is important to note that this pipeline does not necessarily capture the evolutionary history of the family and its members.