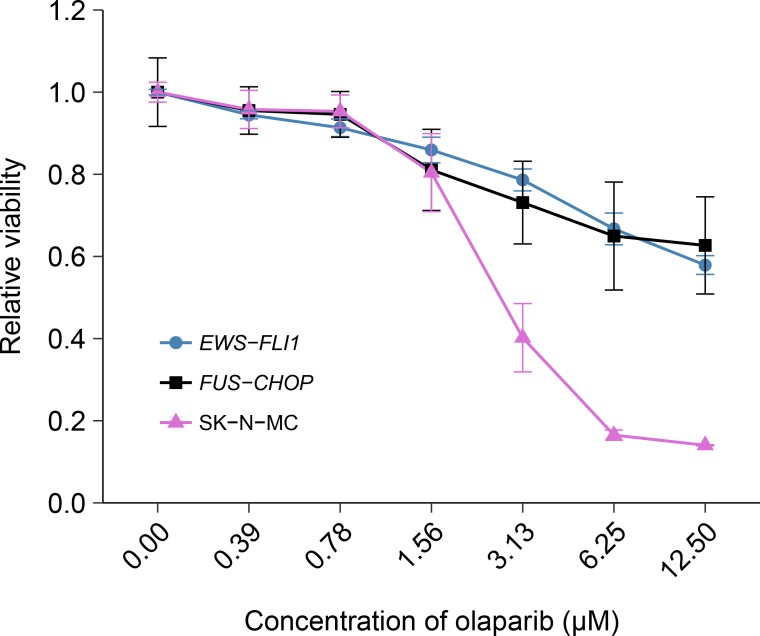
Figure 2. Olaparib sensitivity in cells transformed with the EWS-FLI1 rearrangement.
Cell viability assays were performed for EWS-FLI1 and FUS-CHOP transformed mouse mesenchymal cells, as well as the human Ewing’s sarcoma cell line (SK-N-MC), which harbors the EWS-FLI1 fusion. Cells were treated with the indicated doses of olaparib and 72 hr later cell viability was determined. Relative viability was calculated as a percentage of vehicle control treated cells. Means reported and error bars represent SD from three independent biological repeats. Additional details for this experiment can be found at https://osf.io/t3dm6/.