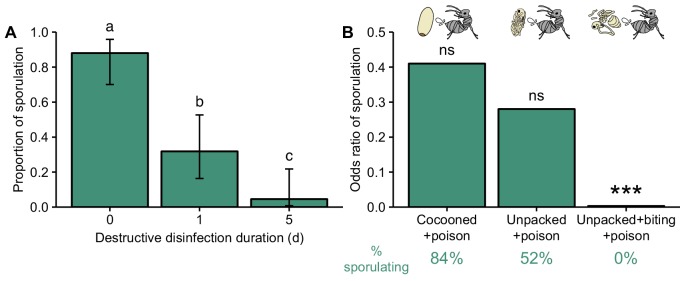
Figure 3. Destructive disinfection by ants prevents pathogen replication.
(A) Destructive disinfection greatly reduced the probability of pupae sporulating compared to pupae that received no destructive disinfection (time point 0), and its effectiveness increased with the length of time ants could perform destructive disinfection (1 vs. 5 days; error bars show ± 95% CI; letters denote groups that differ significantly in Tukey post-hoc comparisons [p<0.05]). (B) The individual components of destructive disinfection (unpacking, biting and poison spraying) interacted to inhibit pathogen replication (% of pupae sporulating in each treatment shown under graph in green). The odds of sporulation for cocooned and unpacked pupae treated with poison were not significantly different to those of control pupae (cocooned pupae treated with water). But when unpacking, biting and poison spraying were combined, the odds of sporulation were significantly reduced (logistic regression; ns = non-significant deviation from control, ***=p<0.001; complete data set of full factorial experiment displayed in Figure 3—figure supplement 3 and all statistics in Table 3).
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Destructive disinfection of infected pupae in small groups of ants is less efficient.
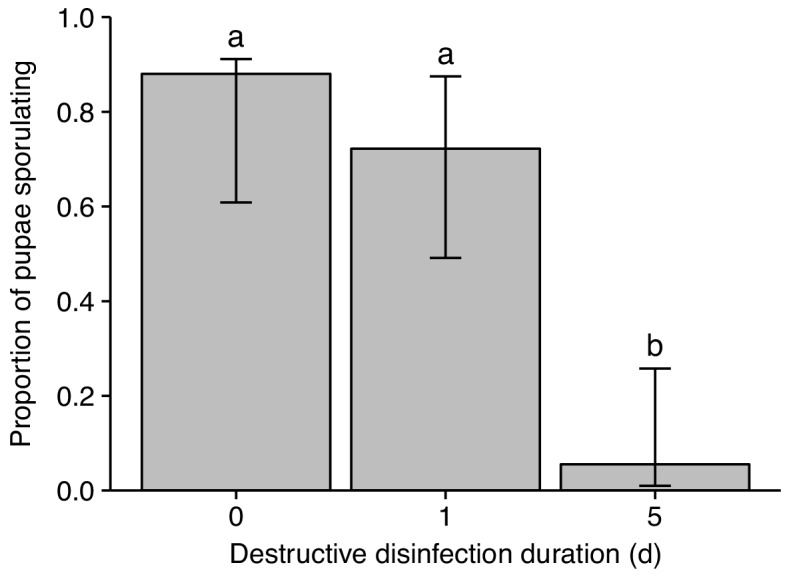
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Comparison of ant and synthetic poison spraying.
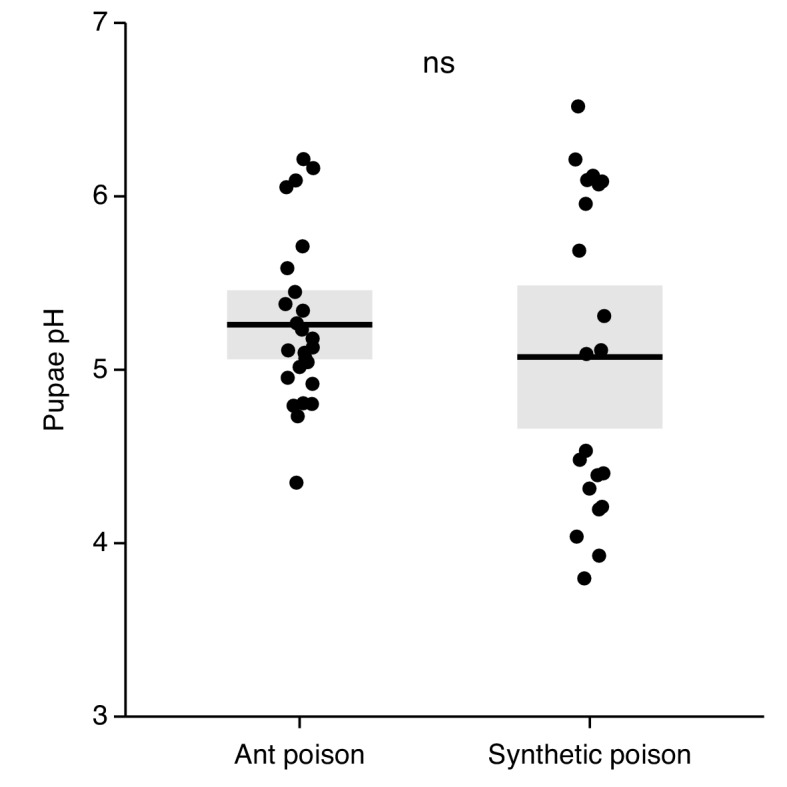
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Destructive disinfection by ants prevents pathogen replication.
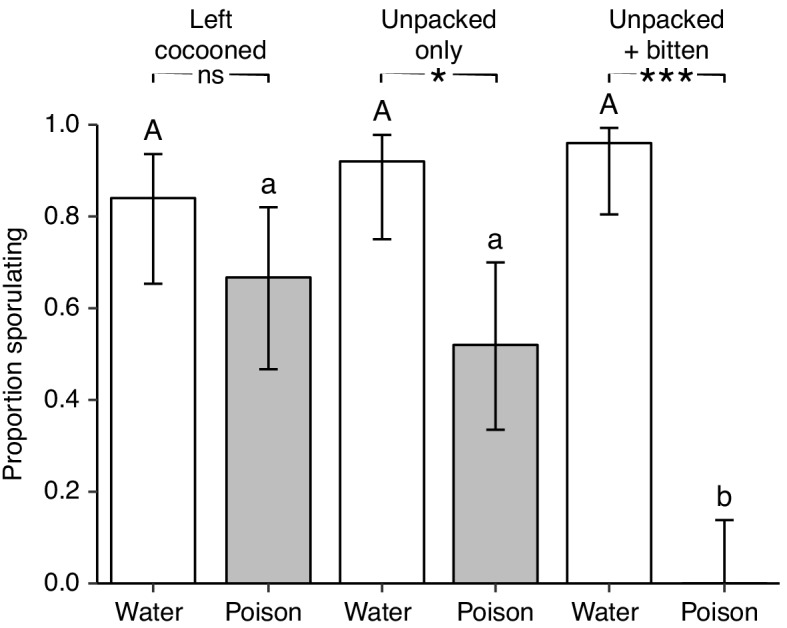
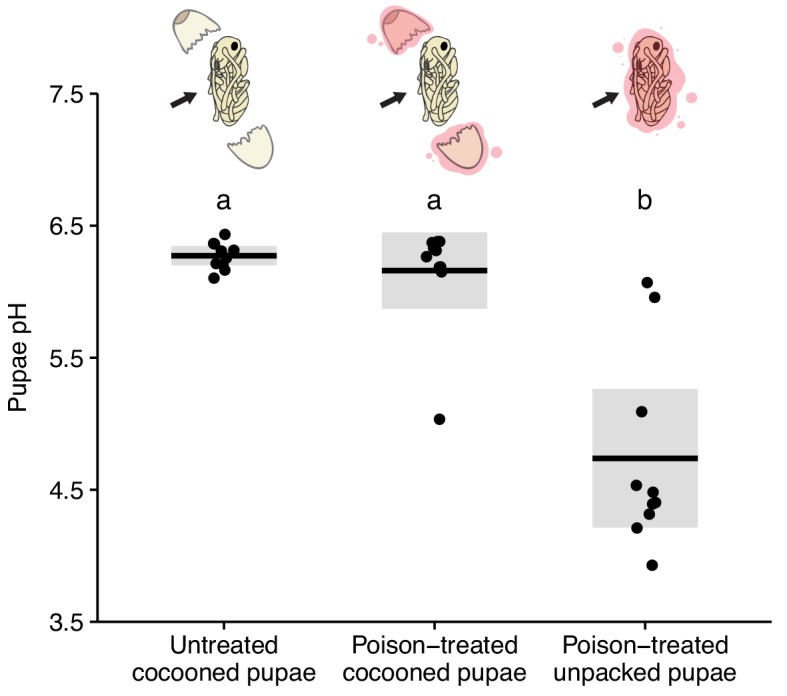
Figure 3—figure supplement 4. The pupal cocoon blocks the application of poison.