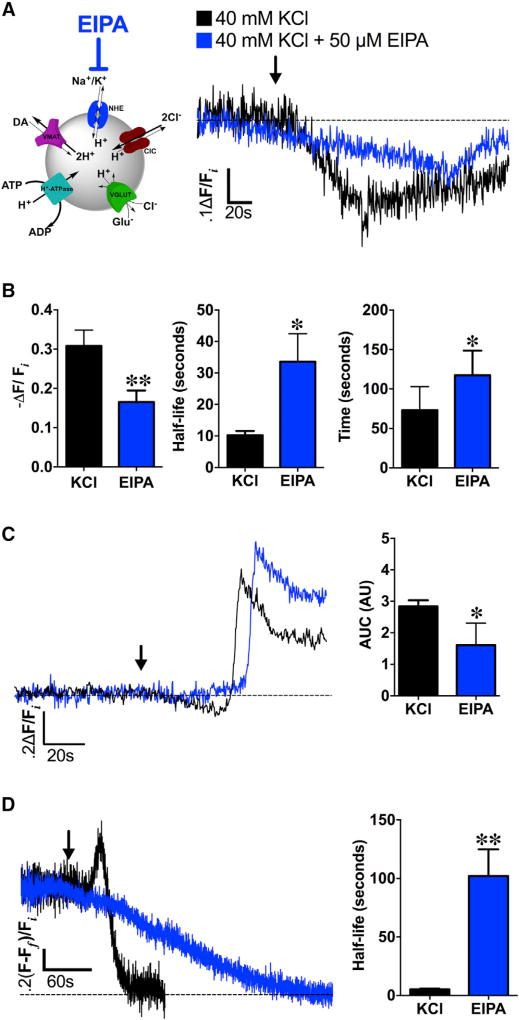
Figure 6. NHEs Mediate Depolarization-Induced Changes in SV pH and DA Content.
(A) Left: schematic illustrating NHE inhibition by EIPA during high K+ stimulation (40 mM KCl). Right: averaged dVMAT-pHluorin fluorescence traces measuring changes in SV pH during KCl stimulation in brains pre-treated with NHE inhibitor EIPA (50 µM, 15 min; blue trace, n = 5 flies) compared to high K+ stimulation alone (black trace, n = 8).
(B) EIPA pre-treatment (n = 5) significantly decreased the magnitude of depolarization-induced SV hyperacidification compared to the non-EIPA control (n = 8; p = 0.02). EIPA pre-treatment also delayed the timing (t = 117.5 ± 14.0 s; p = 0.03) and kinetics (t1/2 = 33.6 ± 8.9 s; p = 0.004) to reach maximal vesicle acidification compared to the non-pretreated control.
(C) In the absence of TeTxLC expression in DA terminals, EIPA still attenuated SV hyperacidification preceding KCl-induced exocytic SV fusion (blue trace, n = 5) compared to the non-pretreated control (black trace, n = 6; p < 0.05); duration and magnitude of SV hyperacidification is represented as area under the curve (AUC). Curves represent average dVMAT-pHluorin fluorescence traces.
(D) Left: EIPA pre-treatment abolished depolarization-induced increases in DA vesicle loading in presynaptic DA nerve terminals (blue trace; n = 4) compared to non-pretreated controls (black trace; n = 4). Right: EIPA pre-treatment significantly slowed FFN206 vesicle destaining (t1/2=102.1±22.8 s; n=4) compared to non-EIPA pre-treated controls (t1/2 = 5.2 ± 0.9 s, n = 4; p = 0.005) as fit to a monoexponential decay.
An ~60 s baseline was recorded prior to KCl application (indicated by arrow). Unpaired t tests: (B)–(D). Error bars, SEM. Fly strains: (A) and (B): TeTxLC; TH-GAL4, UAS-dVMAT-pHluorin; (C): +; TH-GAL4, UAS-dVMAT-pHluorin; (D): dVMATP1; TH-GAL4, UAS-dVMAT.