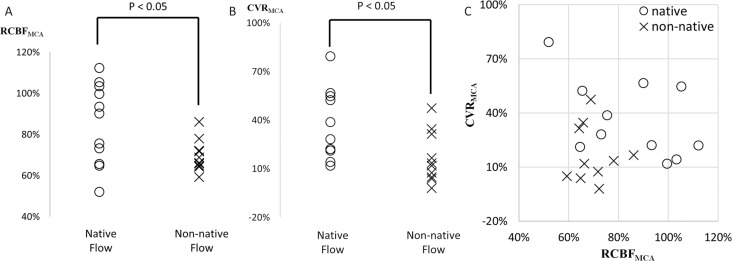
Fig. 2.
Comparison of rest cerebral blood flow (CBF) (A), cerebral vascular reserve (CVR) (B) and both combined (C) in the territory of middle cerebral artery (MCA) between the native and non-native, retrograde, flow in the affected-side the ophthalmic artery (OphA). Rest cerebral blood flow to normal control (RCBFMCA), the ratio of rest CBF in the affected-side MCA territory to the default value obtained from healthy participants; CVRMCA, The cerebral vascular reserve in the affected-side MCA territory calculated by dividing (stress CBF – rest CBF) by the rest CBF. High-risk patients were defined based on the previous large cohort study (RCBFMCA < 80% and CVRMCA < 10%).