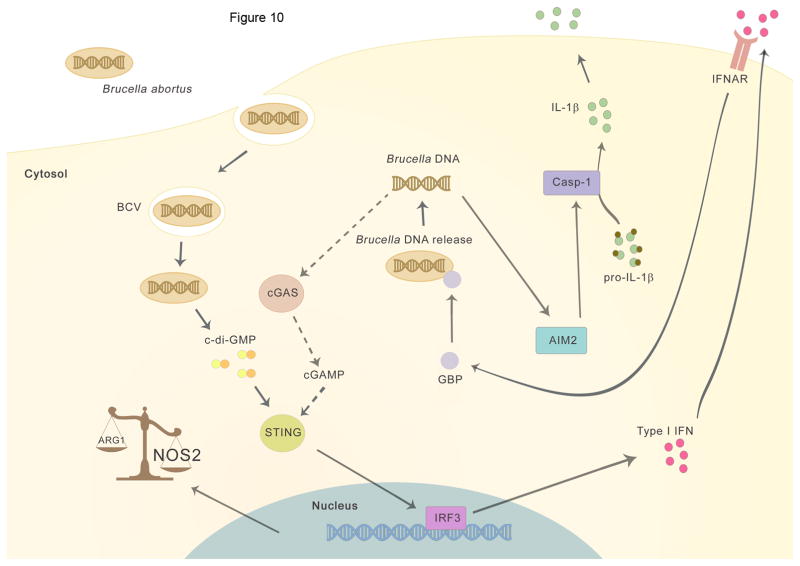
Figure 10. Working model.
The intracellular bacteria Brucella abortus enters the host cell and ensures its survival by forming the Brucella-containing vacuole (BCV). Initially, the recognition of bacterial c-di-GMP activates STING and triggers type I interferon response and upregulation of NOS2 and GBPs expression. GBPs promote lysis of the BCV by exposing bacterial components, like bacterial DNA in the cytosol, thus enabling activation of AIM2 and IL-1β secretion. Additionally, release of Brucella genomic DNA in the cytosol may activate cGAS generating cGAMP (dotted line) resulting in further amplification of type I IFN signaling pathway.