Figure 2. PKA is required for vasoconstriction of cerebral parenchymal arteries in response to elevated glucose.
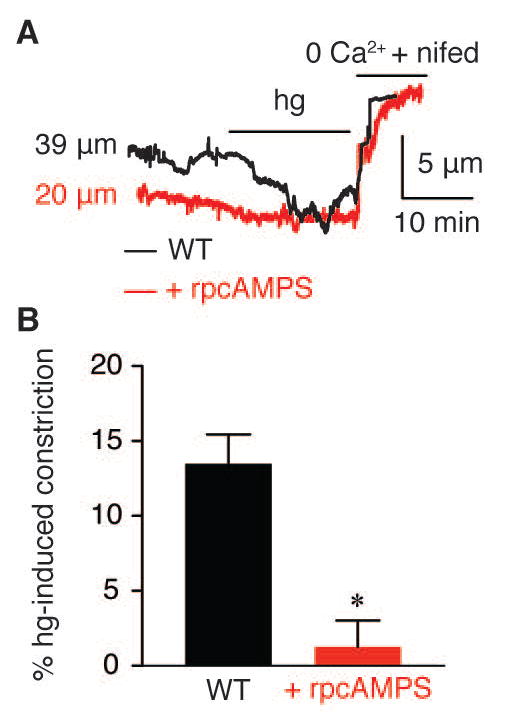
A) Representative diameter recordings and B) summary hg-induced constriction in the absence or presence of the PKA inhibitor rpcAMPs (10 μM). A solution containing 0 mM extracellular Ca2+ and the LTCC blocker nifedipine (1 μM) was used to obtain the passive diameter. *P < 0.05.
