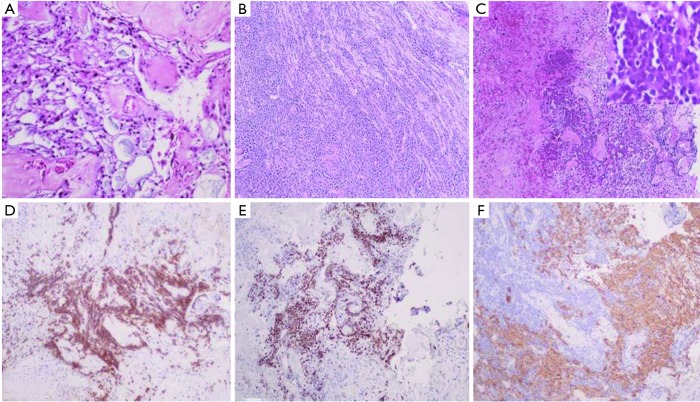
Figure 2.
Histological and immunohistochemical examination. This shows glial tumour cells arranged in a papillary manner around vascularized mucoid stromal cores (A, Haematoxylin-eosin-saffron ×200). A nerve adjacent to the ependymoma was massively invaded by a lymphoid proliferation (B, Haematoxylin-eosin-saffron ×200). The lymphoid proliferation infiltrated the ependymoma (C, Haematoxylin-eosin-saffron ×200) and was composed of large lymphoid cell (C, right picture ×400). The lymphoid cells expressed the B lymphoid marker CD20 (D, CD20 immunostaining ×100) and were highly proliferative (E, Ki67 immunostaining ×100) contrasting with indolent (E), GFAP positive cells of the myxopapillary ependymoma (F, GFAP immunostaining ×100). GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.