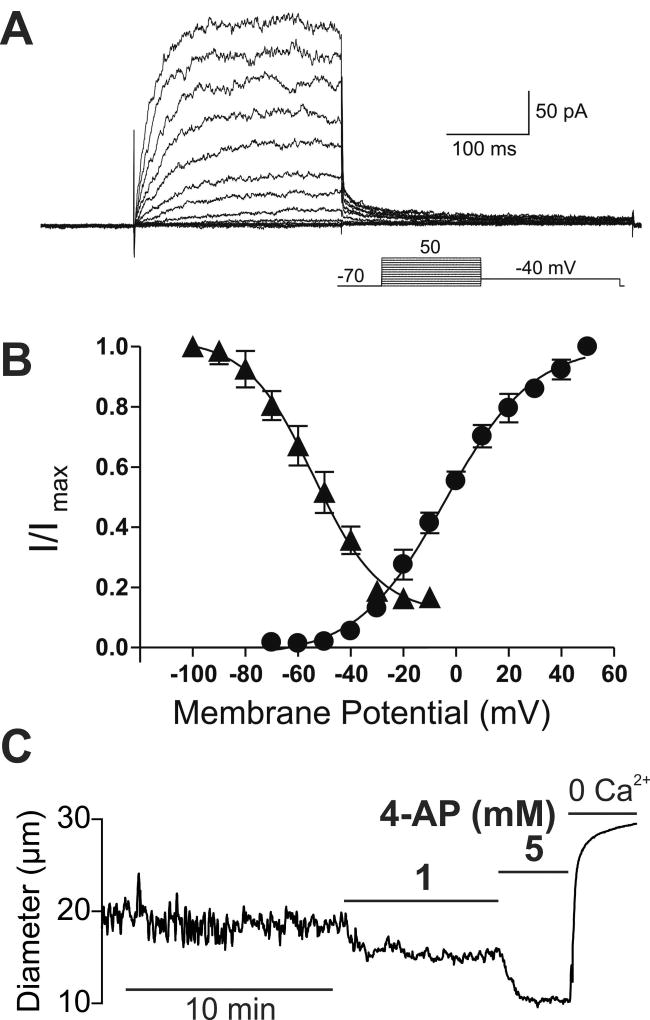
Figure 1. KV channels exert a tonic dilatory influence on the diameter of intracerebral arterioles.
(A) Families of KV currents from an isolated arteriolar smooth muscle cell elicited by voltage pulses from −70 mV to +50 mV in the presence of 100 nM iberiotoxin to inhibit large conductance (BK) currents. (B) steady-state activation (circles) and inactivation (triangles) properties of KV currents measured from isolated arteriolar smooth muscle cells. Solid lines, Boltzmann fits to the data. (C) Typical recording of the internal diameter of a pressurized parenchymal arteriole (40 mm Hg) showing the constriction caused by the perfusion of the KV blocker 4-AP, 1 and 5 mM. A and B are from (58) and C is from (17).