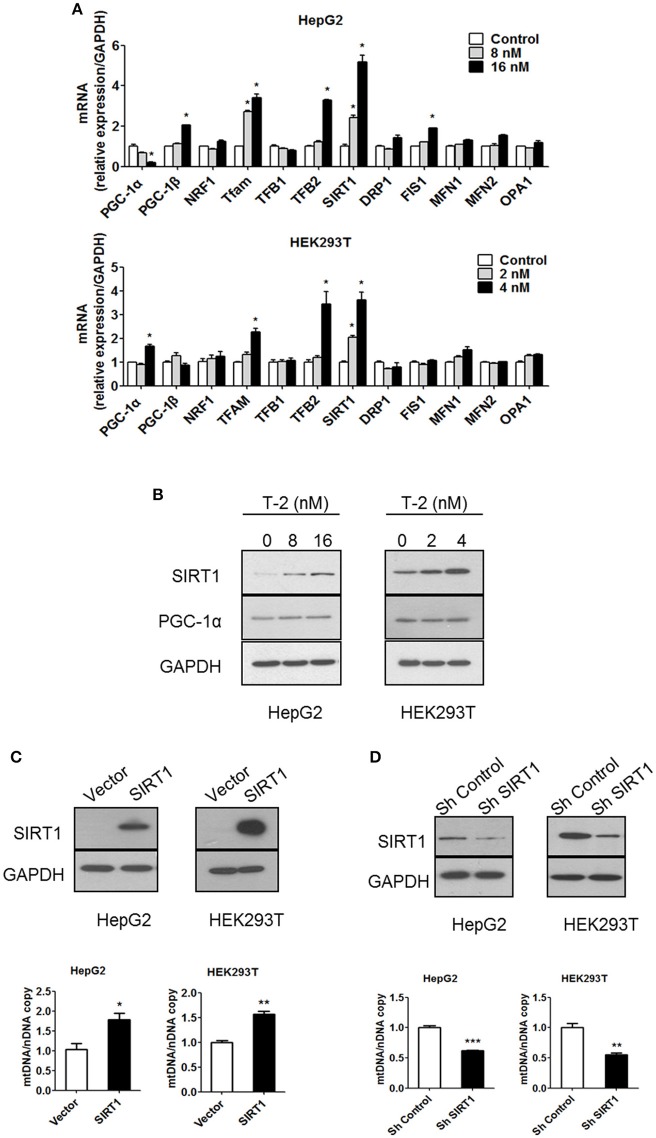
Figure 3.
Low-dose exposure to T-2 toxin enhanced the mRNA and protein levels of SIRT1 in HepG2 and HEK293T cells. (A) PGC-1α, PGC-1β, NRF1, TFAM, TFB1, TFB2, SIRT1, DRP1, FIS1, MFN1, MFN2, and OPA1 mRNA levels in HepG2 (top) and HEK293T cells (bottom panel) were analyzed by RT-qPCR after T-2 toxin exposure at different doses. All the tested mRNA levels were normalized by the GAPDH mRNA level as the internal control. The experiments were repeated at least three times. (B) The protein levels of SIRT1, PGC-1α, and GAPDH in HepG2 (Left) and HEK293T cells (Right) with or without T-2 toxin treatment were assayed by western blotting with antibodies against SIRT1, PGC-1α, and GAPDH, respectively. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) SIRT1 expression level in HepG2 and HEK293T cells overexpressing SIRT1 was analyzed by western blotting. Mitochondrial DNA content in HepG2 and HEK293T cells overexpressing SIRT1 analyzed by RT-qPCR. (D) SIRT1 expression level in HepG2 and HEK293T cells infected with SIRT1 or nontargeting shRNA was analyzed by western blotting. Mitochondrial DNA content in HepG2 and HEK293T cells stably transfected with SIRT1-specific shRNA or nontargeting shRNA was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Statistically significant differences are indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).