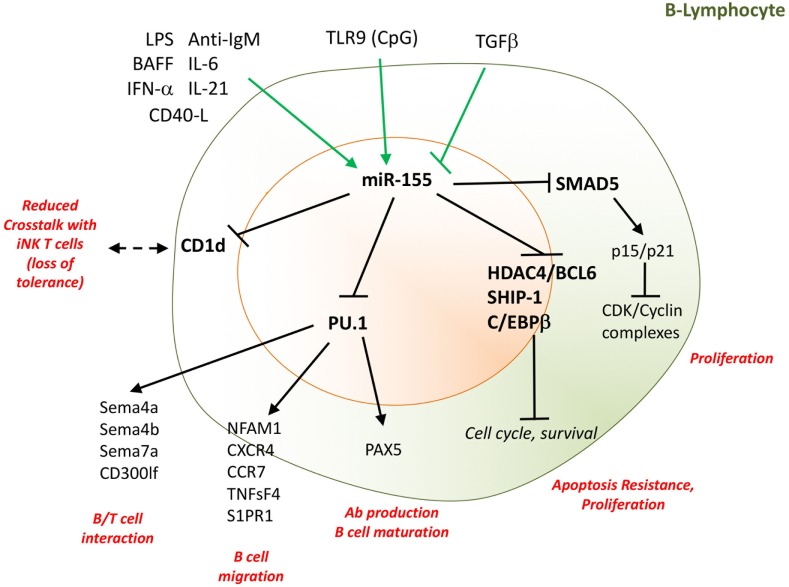
Figure 3.
miR-155 supports B-cell proliferation and antibody production. Several cytokines and TLR-ligands can induce miR-155 expression in B-cells. These include LPS, IL-6, IL-21, CD40L, IFN-α, and BAFF, while TGFβ inhibits miR-155 expression. By targeting SHIP-1, C/EBPβ, the Hdac4/Bcl6 complex, and the TGFβ signaling molecule SMAD5, miR-155 drives proliferation and resistance to apoptosis of B-cells. miR-155, by epigenetic regulation of PU.1, is indispensable for B-cell maturation, migration, interaction with T-cells, and antibody production. Moreover, miR-155 regulates the surface expression of CD1d on B-cells, influencing the cellular cross talk with invariant NK T-cells. Direct targets are marked in bold font. LPS, lipopolysaccharides; IL, interleukin; TLR, toll-like receptor; Bcl, B-cell lymphoma; SMAD5, small mother against decapentaplegic 5; CD, cluster designation; PU.1, Spi-1 Proto-Oncogene; Sema, semaforin; NK, natural killer; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; CD40L, CD40 ligand. TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; SHIP-1, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1; Bcl6, B-cell lymphoma; HDAC4; histone deacetylase 4; C/EBPβ: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta; NFAM1, NFAT activating protein with ITAM motif 1; CXCR4; C–X–C chemokine receptor type 4; CCR7, C–C chemokine receptor type 7; S1Pr1, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; TNFsF4, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4; CD300lf, CMRF35-like molecule 1.