Figure 5.
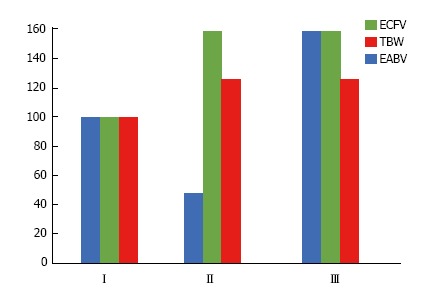
Percent changes from normal of body fluid compartments in hypervolemic states. I: Normal body fluid state; II: Congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome with underfill mechanism of fluid retention; III: Nephrotic syndrome with overfill mechanism of fluid retention. EABV: Effective arterial blood volume; ECFV: Extracellular fluid volume; TBW: Total body water.
