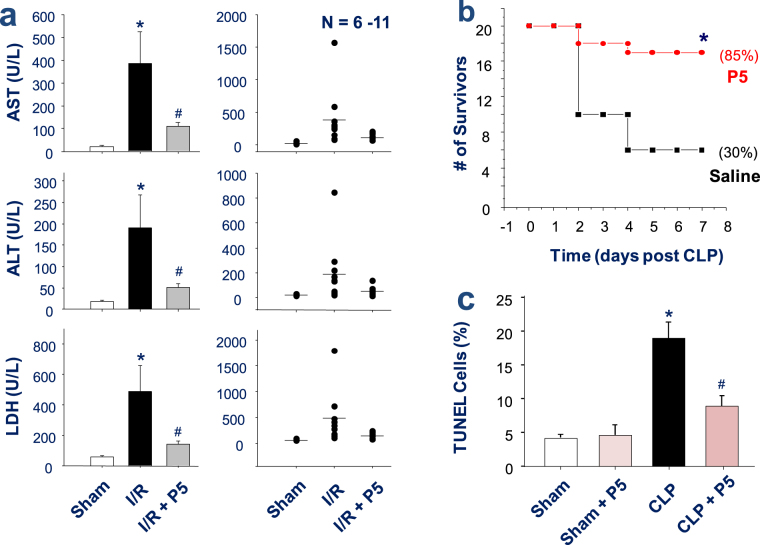
Figure 7.
P5 peptide significantly protected mice against hepatic I/R injury and lethal sepsis. (a) P5 peptide conferred a significant protection against hepatic I/R injury. Male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to hepatic ischemia and intravenously administered with 0.2 ml saline or P5 peptide solution (10.0 mg/kg BW) at the onset of reperfusion. At 24 h after the onset of ischemia, animals were euthanized to harvest blood to measure serum markers of hepatic injury (e.g., AST and ALT) and LDH. *P < 0.05 versus “Sham control”; # P < 0.05 versus Saline group (“I/R”). (b) P5 peptide protected mice against lethal sepsis. Male Balb/c mice were subjected to lethal sepsis by CLP, and intraperitoneally administered with control saline (0.2 ml/mouse) or P5 peptide (8.0 mg/kg) at +2, +24 hours post CLP. Animal survival was assessed for up to two weeks, and the Kaplan-Meier method was used to compare the differences in mortality rates between groups. *P < 0.05 versus “CLP + Saline” group. (c) P5 peptide reduced TUNEL-positive staining in the lungs of septic animals. The lungs of septic mice were harvested at 24 h post CLP, and tissue sections were stained by TUNEL staining and DAPI. The number of TUNEL-positive green cells was expressed as an average percentage of total DAPI-positive blue cells in 5–8 randomly selected fields. *P < 0.05 versus “Sham” control; # P < 0.05 versus “CLP” group.