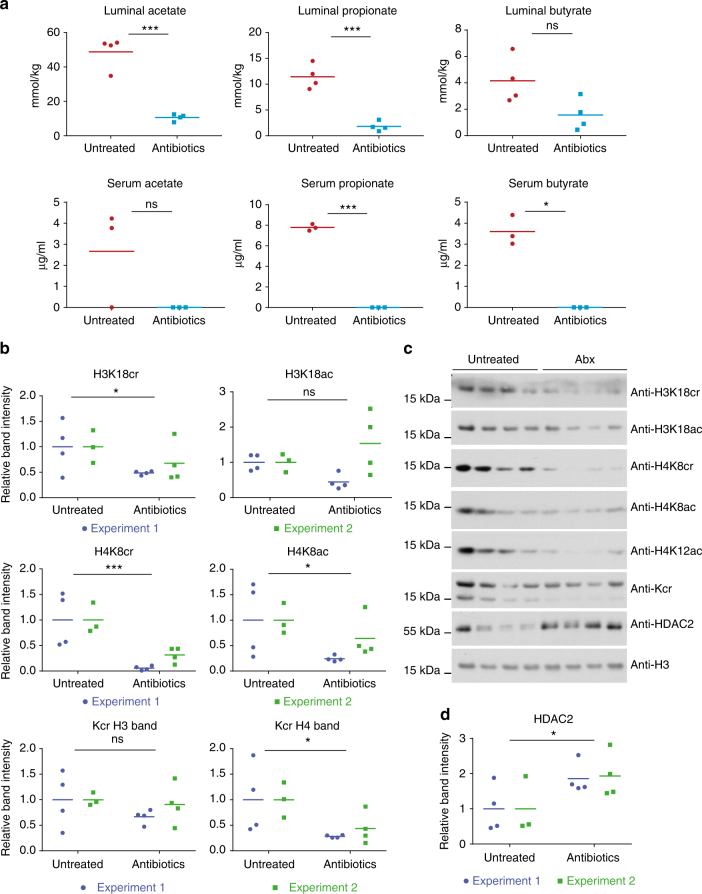
Fig. 3.
Microbiota depletion affects colonic histone crotonylation and HDAC2. Antibiotic treatment led to a decrease in luminal and serum SCFA levels in mice (n ≥ 3, from experiment 2). a Acetate, propionate, and butyrate concentrations were measured in the colon lumen and serum by gas chromatography. Unpaired t-tests were conducted, *p-value < 0.05 and ***p-value < 0.001. Values of zero were below detectable levels. b Quantifications of western blot analysis of colon extracts from untreated and treated mice, n ≥ 3. Experiments 1 and 2 are repeat experiments. Center values (small bar) are the average of the treatment group relative to the untreated group. Two-way ANOVA (two-tailed) was performed on quantified bands to compare the effect of treatment for both experiments together; * corresponds to a p-value of < 0.05 and *** corresponds to <0.001. The quantification showed a statistically significant decrease in H4 crotonylation as detected by the anti-Kcr antibody and in H4K8cr, H4K8ac, and H3K18cr levels upon antibiotics treatment. c Global changes in various colon histone crotonylation and acetylation marks and HDAC2 as seen in representative western blots of colon extracts, from experiment 1. d Two-way ANOVA was performed on quantified bands from western blotting analysis with anti-HDAC2. A statistically significant increase was observed (p-value < 0.05)