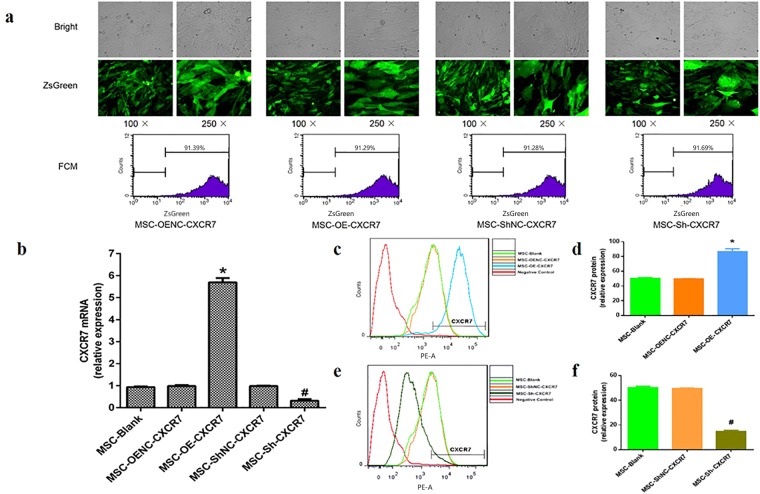
Figure 1.
Long-term transgene expression efficiency in mMSCs after lentiviral vector transduction. (a) The mMSCs were transduced separately with pHBLV-CMVIE-CXCR7-ZsGreen-T2A-Puromycin (MSC-OE-CXCR7), pHBLV-CMVIE-ZsGreen-T2A-Puromycin (MSC-OENC-CXCR7), pHBLV-U6-ShRNA-ZsGreen-Puromycin (MSC-Sh-CXCR7) and pHBLV-U6-ZsGreen-Puromycin (MSC-ShNC-CXCR7) lentiviral vectors were cultured for 20 passages and observed with light microscopy (top) and fluorescence microscopy with green fluorescent protein (middle), 100× and 250×; the percentage of ZsGreen-positive cells were analysed by flow cytometry (bottom) at passage 20 after transduction. (b) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis shows CXCR7 mRNA expression in mMSCs after pHBLV-CMVIE-CXCR7-ZsGreen-T2A-Puromycin and pHBLV-U6-ShRNA-ZsGreen-Puromycin transduction. (n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs. MSC-OENC-CXCR7, # p < 0.05 vs. MSC-Sh-CXCR7). (c,d) FCM analysis shows CXCR7 overexpression in mMSCs after transduction. (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. MSC-OENC-CXCR7). (e,f) FCM analysis shows CXCR7 suppression in mMSCs after transduction. (n = 3; # p < 0.05 vs. MSC-ShNC-CXCR7).