Figure 8.
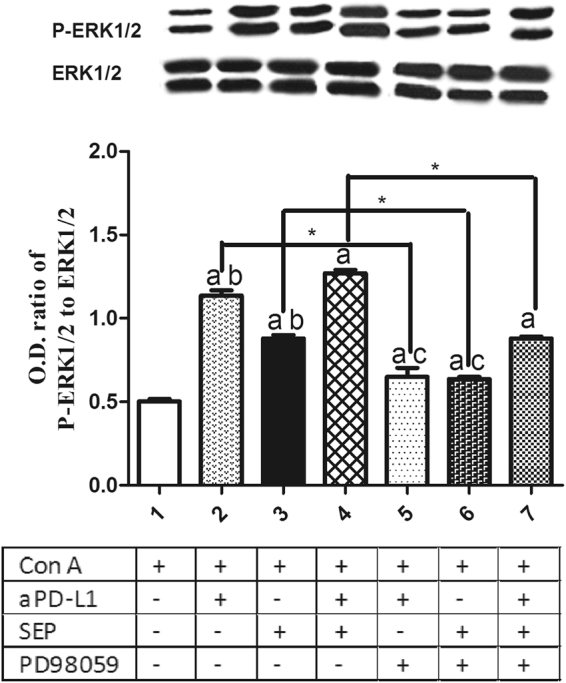
Effects of SEP and αPD-L1 combination on MEK/ERK signaling pathway in T lymphocytes in vitro. The T cells from naïve mice were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum. After the cells were pretreated with/without MEK inhibitor PD98059 (40 μM) for 30 min, they were cultured with the aPD-L1 (10 nM) and/or SEP (50 μg/ml) with ConA (2 μg/ml) for additional 48 h. The T cells were collected and lysed in lysis buffer supplemented with a cocktail of protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Western blot analysis was conducted for the detection of P-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 expression. αPD-L1 or SEP in combination with ConA significantly increased the ratios of P-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 compared with ConA group (P < 0.05, respectively, n = 3). Furthermore, combination of SEP and αPD-L1 had more potent than SEP (P < 0.05, n = 3) or αPD-L1 (P < 0.05, n = 3). However, after the pretreatment with PD98059 for 30 min, the the increased ratios induced by SEP or/and αPD-L1 was partially decreased (P < 0.05, respectively, n = 3). The results were presented as mean ± SEM. a P < 0.05 compared with control group. b P < 0.05, compared with SEP and αPD-L1 combination group (group 4). c P < 0.05, compared with SEP and αPD-L1 combination group after PD98059 pretreatment for 30 min (group 7). * P < 0.05, group 2 compared with group 5; group 3 compared with group 6; group 4 compared with group 7.
