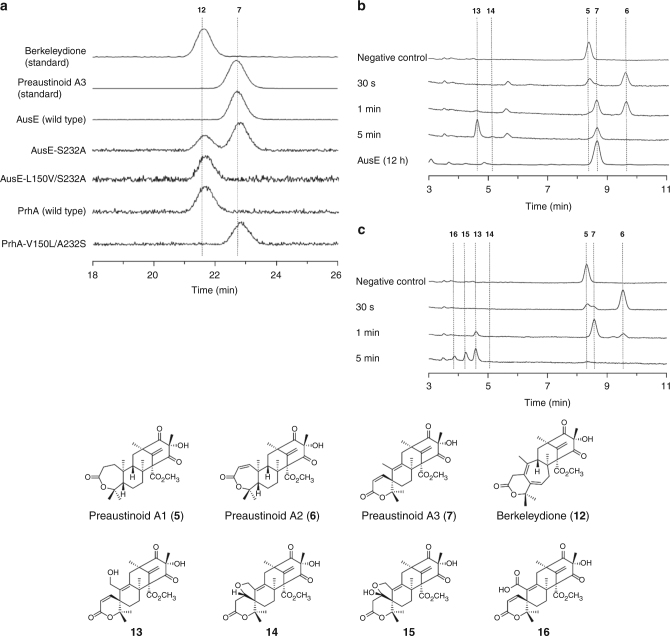
Fig. 3.
In vitro enzyme reactions of the wild-type and mutant AusE and PrhA with preaustinoid A1 (5). a LC-MS extracted ion chromatograms of 12 and 7 (m/z 457.2) in the in vitro enzymatic reactions of 5 and wild-type AusE, AusE-L150V, AusE-L150V/S232A, wild-type PrhA, or PrhA-V150L/A232S. All of the reactions were performed for 5 min. b, c HPLC chromatograms of in vitro enzymatic reactions of 5 and PrhA-V150L/A232S (b) or PrhA-V150L/A232S/V241M (c), respectively. The reactions of PrhA-V150L/A232S and PrhA-V150L/A232S/M241V were performed for 30 s, 1 and 5 min. The reaction of wild-type AusE was performed for 12 h as a reference (b). New peaks corresponding to 13–16 were only observed in the reaction of PrhA-V150L/A232S and PrhA-V150L/A232S/M241V, and not in the reaction of wild-type AusE. HPLC condition optimized for separation of 13–16 was used for analysis. 5 incubated in pH 7.5 PIPES buffer for 12 h in the absence of enzyme was used as a negative control. Chromatograms were monitored at 223 nm