FIG 9 .
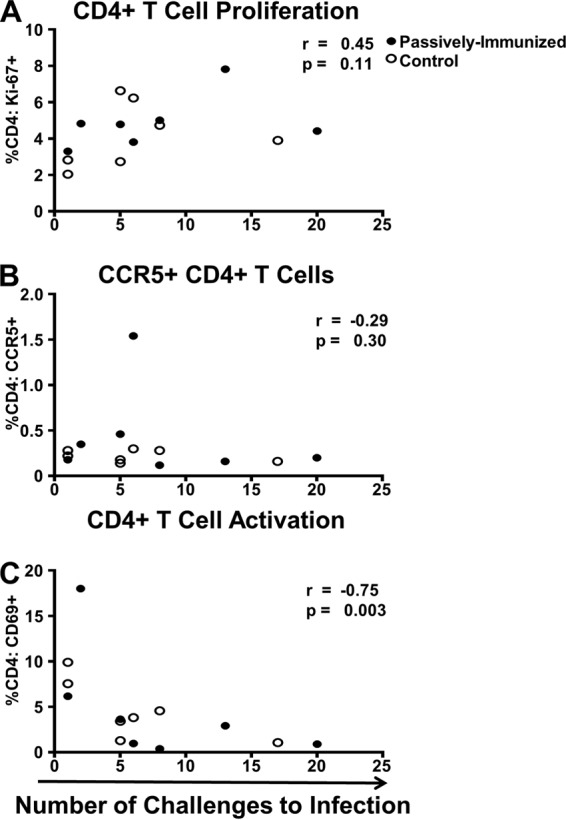
Infant systemic CD4+ T cell activation (CD69+) correlated with a reduced number of challenges to infection. CD4+ T cell proliferation (Ki-67+) (A) and CCR5+ expression (B), shown for all infants, did not show evidence of a correlation. Interestingly, CD4+ T cell activation (C) exhibited a strong correlation with a lower number of challenges to infection. Two infants remained uninfected at challenges 17 and 20. Passively immunized infants are represented by closed circles; control infants are represented by open circles.
