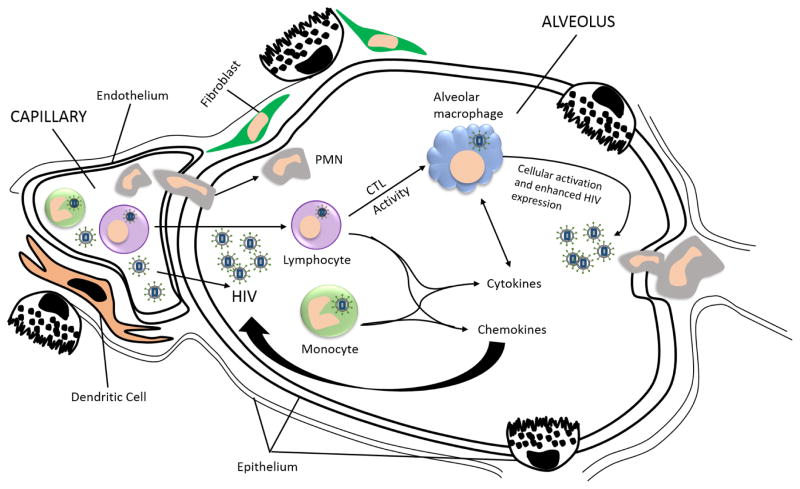
Figure 3.
Immune reactions to HIV in the alveolar space. The presence of HIV-infected cells, or free virus, in lung tissue stimulates an adaptive immune response and the recruitment of HIV-specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs). These CTLs accumulate in the alveolar space and release pro-inflammatory cytokines that further activate alveolar macrophages to release additional cytokines leading to further inflammatory cell recruitment. When infected with HIV, alveolar macrophages are compromised in binding and recognizing pathogen and the level of CD4 T cells is decreased.