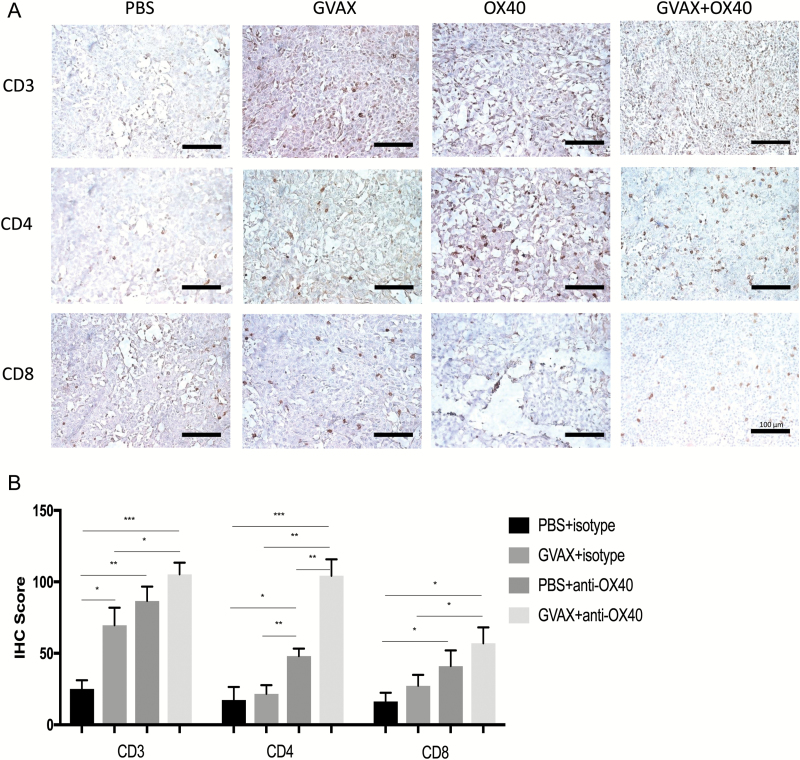
Fig. 3.
(A) Immunohistochemistry with staining for CD3, CD4, and CD8. Brain and tumor specimens derived from untreated hosts show scant lymphocytic infiltration with relative increases in all 3 markers after either vaccination or anti-OX40 monotherapy. Qualitatively, it is apparent that inflammation is greatest in the tumors harvested from animals treated with combination GVAX and anti-OX40 immunotherapy, particularly in the CD4+ subset. All images are magnified 20× (bar within photomicrographs is 100 microns in length). (B) Histoscores derived from counts by blinded analysts confirm the impression that combination GVAX + agonist anti-OX40 immunotherapy increased the numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ intratumoral lymphocytes. Both the magnitude and the statistical significance were greatest in the CD4+ subset. (***P < 0.0005, **P < 0.005, *P < 0.05; absence of an asterisk denotes not significant comparison.)