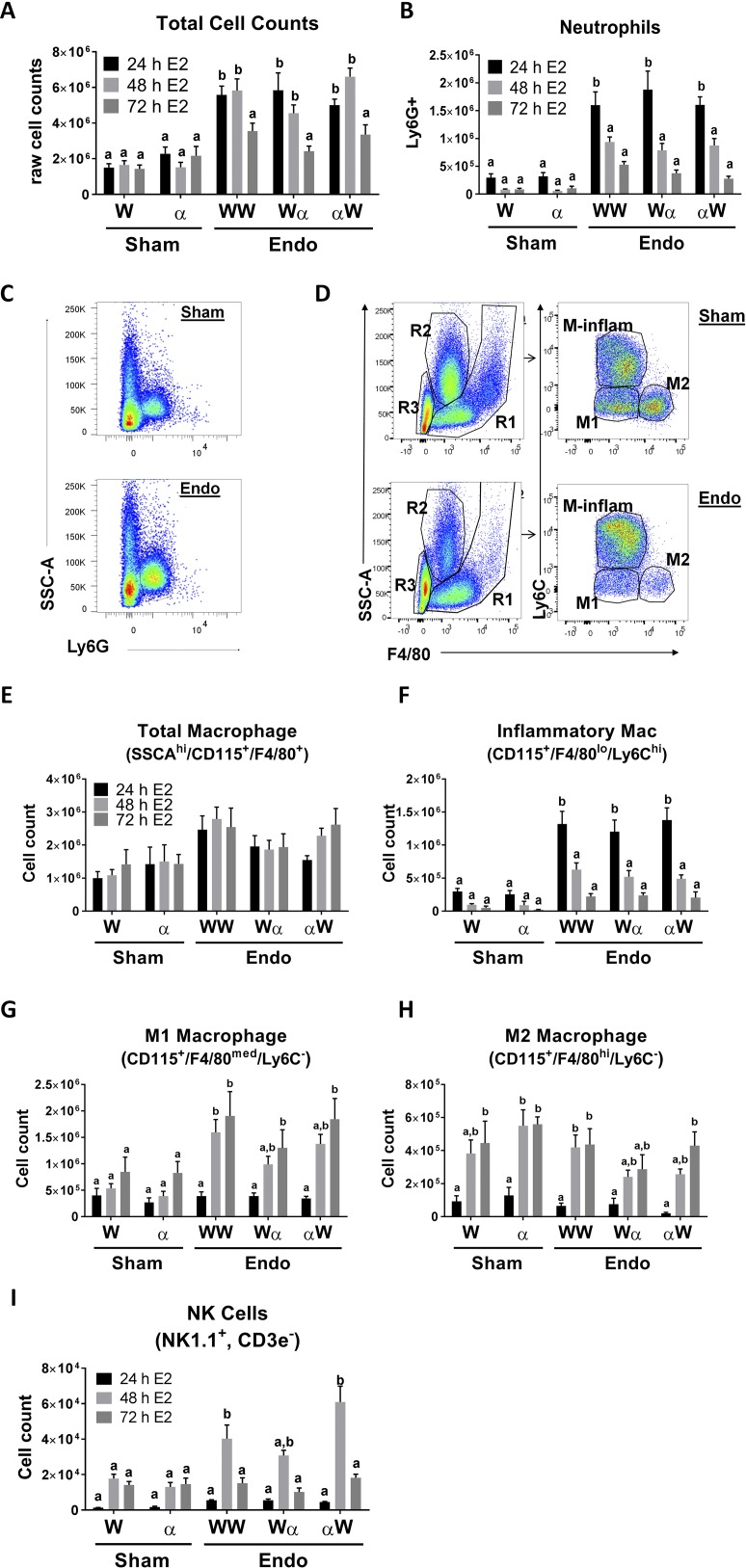
Figure 4.
Innate immune cells infiltrate into the peritoneal cavity after the initiation of endometriosis in a disease-dependent manner. (A) Total cell counts in sham WT (W), sham αERKO (α), endometriosis (endo) WT to WT (WW), endo WT to αERKO (Wα), and endo αERKO to WT (αW) 24, 48, and 72 hours after the initiation of endometriosis. A representative experiment is shown (n = 5). (B) Quantitation of peritoneal neutrophil counts. A representative experiment is shown (n = 5). (C) Neutrophils were gated for Ly6G+. (D) Macrophage gating strategy. Regions (R1, R2, and R3) were gated. R1 was then gated for F4/80+ and Ly6C+ to determine M1, M2, M-inflammatory (M-inflam) macrophages. (E) Quantitation of total macrophages (SSCAhi/CD115+,F4/80+). (F) Quantitation of inflammatory macrophages (SSCAhi/CD115+,F4/80lo/Ly6Chi) (n = 8 to 12). (G) Quantitation of M1 macrophages (SSCAhi/CD115+,F4/80med/Ly6C−) (n = 8 to 12). (H) Quantitation of M2 macrophages (SSCAhi/CD115+,F4/80+/Ly6C−) (n = 8 to 12). (I) Quantitation of NK cells (NK1.1+,CD3e−). A representative experiment is shown (n = 5). Means not sharing a letter are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05). Means sharing a same single letter or a letter in combination with other letters are not significantly different from each other (P > 0.05; two-way ANOVA). Error bars represent standard error of the mean.