Figure 1.
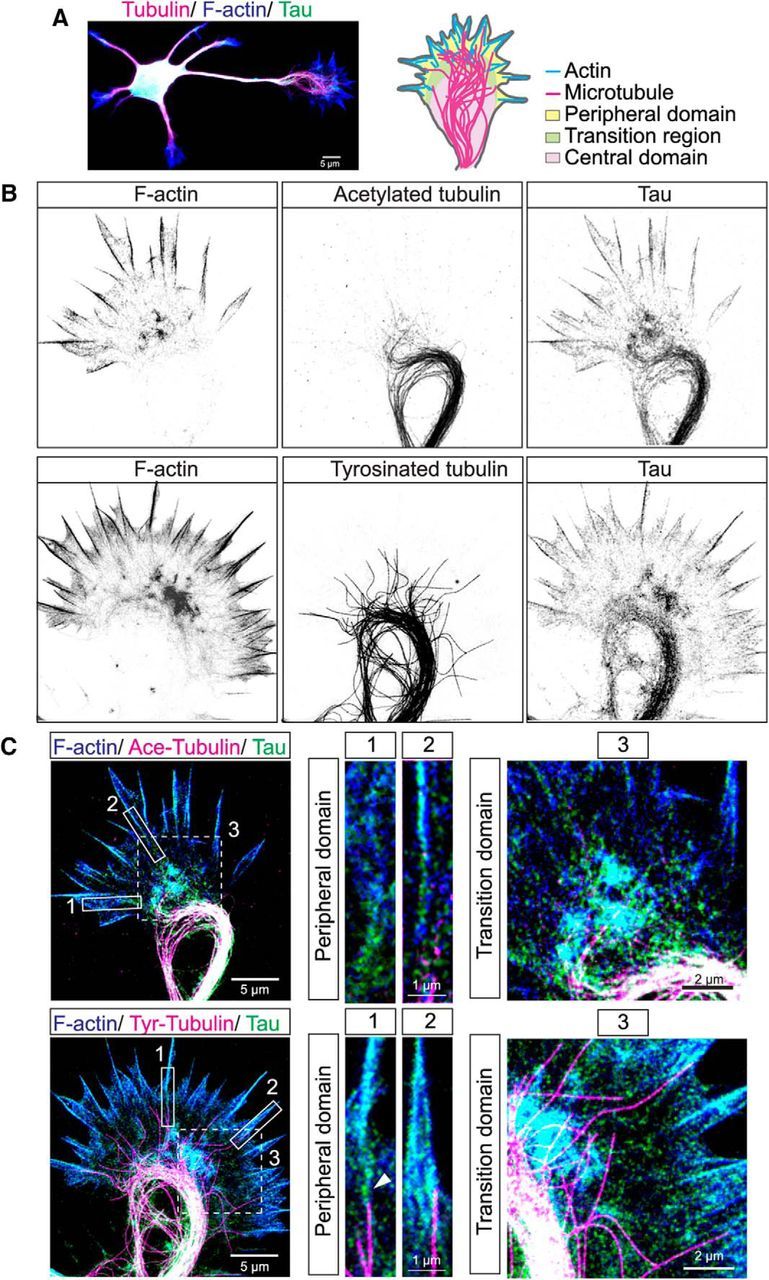
Tau colocalizes with actin filaments as well as with stable and dynamic MTs in central, transition and peripheral regions of hamster cortical growth cones. STED microscopic image of a cortical neuron stained for tau (green), tubulin (magenta), and F-actin (blue) showing multiple dendrites and a single long axon tipped by a growth cone (A). Schematic of the growth cone indicates different domains and positions of the actin and MT cytoskeleton. Two examples of fixed cortical growth cones shown in inverted gray scale (B) and three-color overlay images (C). F-actin (blue) is heavily concentrated in filopodia as well as the transition region between the growth cone center and the periphery. Acetylated stable MTs (magenta) form a prominent bundled loop in the growth cone center. Tyrosinated dynamic MTs also form bundled loops from which individual MTs extend into the transition region and enter filopodia. Tau colocalizes with both F-actin (cyan) and stable and dynamic MTs (white) in all three regions of the growth cone. Three-color insets from boxed regions are higher-magnification images of individual filopodia and of the transition regions. In filopodia tau colocalizes with F-actin and is also positioned at the interface (arrowhead) between a single dynamic MT and an actin filament bundle. Note that acetylated MTs do not extend into filopodia. Insets of the transition region show colocalization of tau and F-actin (cyan) and extension of individual dynamic MTs into this region.
