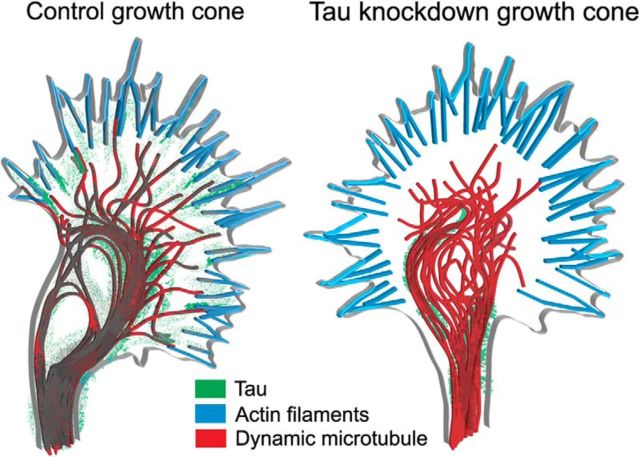
Figure 10.
Schematic summary of results. In a control growth cone (left) tau associates with stable bundled MTs in the center and with dynamic MTs extending into the actin-rich periphery. Tau is also located at the interface between dynamic MTs and actin filaments in filopodia. MT organization and dynamic exploration of the periphery mediated by tau allows growth cones to extend and turn. In a growth cone following tau knockdown (right) MTs fail to form bundles in the center and penetrate only partially into the transition region in disorganized trajectories resulting in defects in axon outgrowth and turning behaviors.