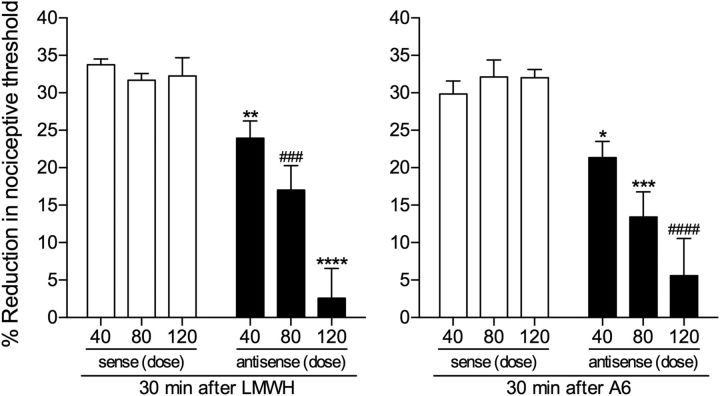
Figure 3.
ODN antisense to CD44 mRNA dose-dependently attenuates LMWH- and A6-induced hyperalgesia. Groups of rats were treated daily with 1 of 3 doses (40, 80, or 120 μg, spinal intrathecal injections) of ODN, antisense (black bars) or sense (white bars) for CD44 mRNA, for 3 consecutive days. On the fourth day, LMWH (left) or A6 (right) (both 1 μg) was injected intradermally on the dorsum of the hindpaw and the mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 30 min later. LMWH and A6 both induced robust hyperalgesia, with no difference between the groups treated with the different doses of CD44 sense ODN (LMWH-treated groups: F(2,15) = 0.4509, p = 0.6454; A6-treated groups: F(2,15) = 0.5264, p = 0.6013, both nonsignificant, when the hyperalgesia in the three groups is compared, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). However, the hyperalgesia induced by LMWH and A6 was dose-dependently attenuated in the groups pretreated with antisense (LMWH groups, 40 μg: t(10) = 3.981, **p = 0.0013; 80 μg: t(10) = 4.337, ###p = 0.0007; 120 μg: t(10) = 6.366, ****p < 0.0001; A6 groups, 40 μg: t(10) = 3.041, *p = 0.0062; 80 μg: t(10) = 4.600, ***p = 0.0005; 120 μg: t(10) = 5.205, ####p = 0.0002, when the respective sense and antisense groups are compared; unpaired Student's t test), with the strongest attenuation observed in the group treated with the highest dose (120 μg), for both LMWH- and A6-induced hyperalgesia. n = 6 paws per group.