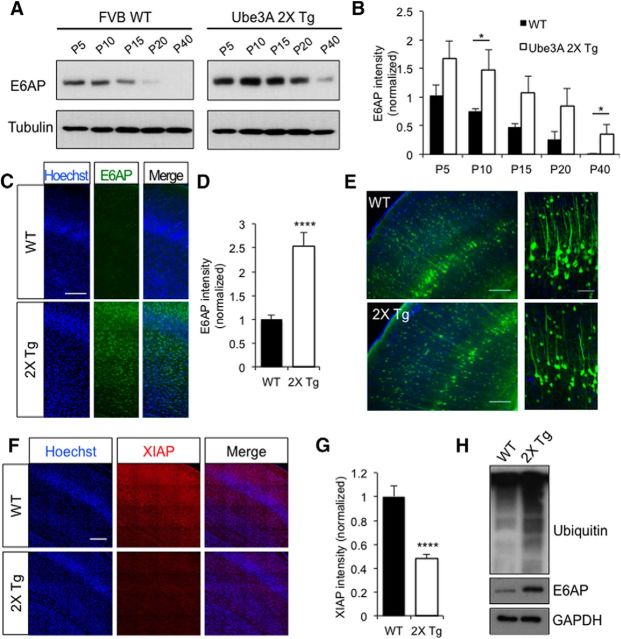
Figure 6.
Increased E6AP overexpression in 2X Tg mice leads to decreased XIAP expression. A, Hippocampal brain lysates were collected from WT or 2X Tg mice from P5 to P40 and E6AP levels were measured by Western blot. Tubulin was probed as a loading control. B, Quantification of E6AP Western blot intensity; n = 3 independent experiments. C, Immunostaining of E6AP in somatosensory cortex slices obtained from P15 WT or 2X Tg mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Quantification showed an increase in E6AP signal intensity in Tg mice; n = 20 slices. E, GFP AAV2 virus was injected into the brain ventricles of WT and 2X Tg mice at P0. Brain slices were prepared at P40 and imaged. Scale bar, 100 μm. A portion of the image of layer-V neurons was enlarged for clarity. Scale bar, 50 μm. Cortical-layer development and neuron density were also analyzed in 2X Tg mice (Fig. 6-1, ). F, XIAP staining in somatosensory cortex slices from P15 WT or 2X Tg mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. G, Quantification showed a decrease in XIAP signal intensity in 2X Tg mice; n = 20 slices. H, MG132 (10 mm, 1.5 μl in each ventricle) was injected into the brain of both WT and 2X Tg mice at P3 for 12 h. Brain lysates were probed for ubiquitin signals. An elevated ubiquitination amount was detected in 2X Tg mice under MG132 treatment. Error bars represent SEM, *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001.