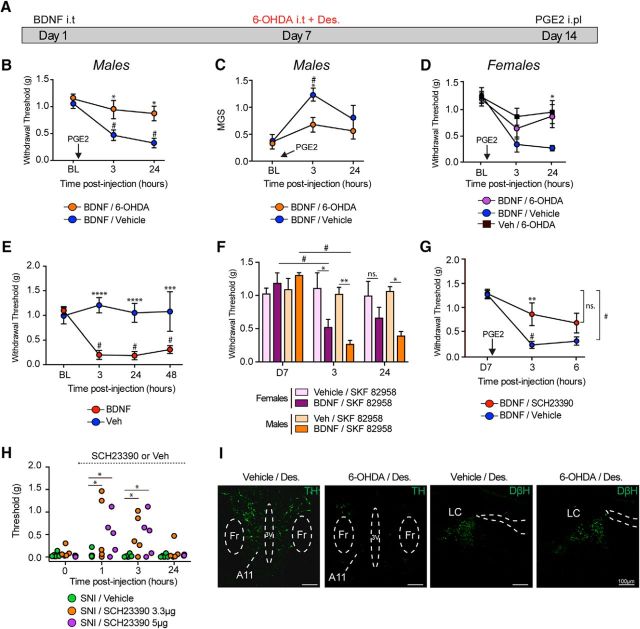
Figure 1.
Spinal DA projections control BDNF-induced hyperalgesic priming and contribute to neuropathic pain. A, Timeline diagram showing 6-OHDA injection in primed mice. B, Subsequent intraplantar injection of PGE2 in mice that were previously treated with BDNF caused mechanical hypersensitivity that lasted for 24 h, whereas DA lesion 7 d after BDNF injection attenuated hyperalgesic priming. N = 6–8 mice per group. C, DA lesion also attenuated PGE2-induced increase in MGS scores in BDNF-primed mice. N = 6–8 mice per group. D, DA lesion also attenuated PGE2-induced allodynia in females BDNF-primed mice. N = 6 or 7 mice per group. E, Intrathecal injection of BDNF produces mechanical hypersensitivity that lasted for at least 48 h. N = 5 or 6 mice per group. F, At day 7, after complete recovery, spinal injection of the D1/D5 agonist in males and females, SKF82958 only reveals priming in animals previously treated with BDNF. N = 5–7 mice per group. G, Intrathecal injection of the D1/D5 antagonist SCH23390 at the time of PGE2 blocks mechanical hypersensitivity in BDNF-primed mice. N = 5 or 6 mice per group. H, Intrathecal injection of the D1/D5 antagonist transiently attenuates neuropathic mechanical allodynia at 1 and 3 h after intrathecal injection. N = 5 or 6 mice per group. I, Intrathecal injection of 6-OHDA reduces A11 hypothalamic DA neurons (6-OHDA + desipramine) without disrupting noradrenergic neurons in the locus ceruleus. Images are representative of N = 3 mice per group. *p < 0.05, comparing WT versus DRD5KO (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). **p < 0.01, comparing WT versus DRD5KO (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). ***p < 0.001, comparing WT versus DRD5KO (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). ****p < 0.0001, comparing WT versus DRD5KO (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). #p < 0.05, compared with baseline (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test).