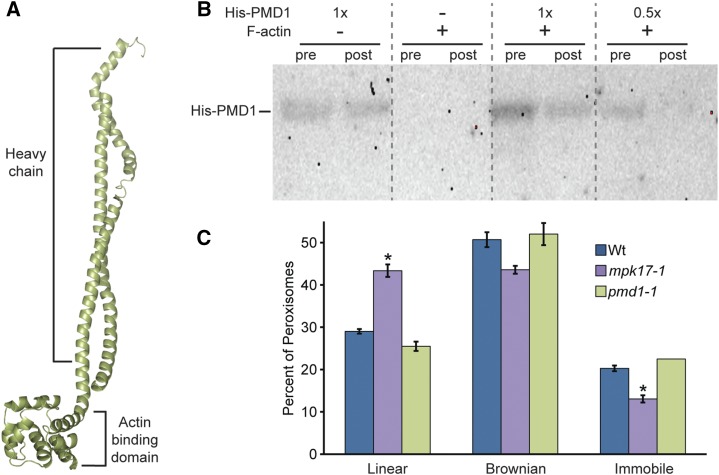
Figure 5.
PMD1 binds actin. A, Phyre2 (Kelley and Sternberg, 2009) predicted structure of PMD1 resembles dynein and myosin H chain proteins. The top portion has high similarity to the coil-coil portion of a H chain, and the bottom domain is highly similar to the actin binding domain, but without a catalytic domain. B, PMD1 binds to actin. Anti-His antibody was used to detect His-PMD11-303 protein in an actin cosedimentation assay. Assays were performed with and without F-actin and the indicated amount of His-PMD11-303 protein. Pre-spin (pre) and post-spin (post) supernatant were used for each lane, as indicated. C, Average percent of peroxisomes in wild type, mpk1-1, and pmd1-1 seedlings carrying the 35S:GFP-PTS1 (Zolman and Bartel, 2004) peroxisome marker grown in unsupplemented media moving in a linear fashion, Brownian fashion, or not moving. Error bars represent the se of the mean. Roots from 7-d-old seedlings were imaged in the maturation zone on the LSM510 (Leica) at a rate of 13 frames/s, for 29 s, then peroxisomes were tracked and the primary type of movement was logged for each peroxisome. At least five individuals of each genotype were imaged, with three images per individual, totaling more than 400 peroxisomes per genotype. mpk17-1 GFP-PTS1 displays a significantly higher percent of linear peroxisome movement than either Col GFP-PTS1 or pmd1-1 GFP-PTS1 (ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD P ≤ 0.05), and a significantly smaller percentage of immobile peroxisomes (ANOVA; P ≤ 0.05). Wt, wild type.