Figure 1.
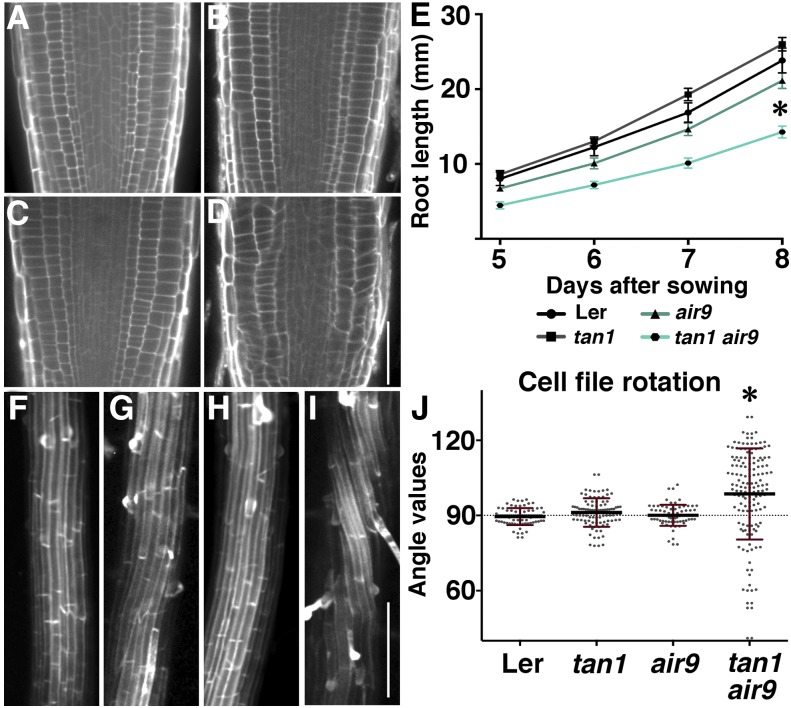
Root phenotypes of Ler, tan1, air9, and tan1 air9 double mutants. A to D, Root cell walls stained with propidium iodide of Ler (A), tan1 (B), air9 (C), and tan1 air9 (D) plants. E, Root length measurements from days 5 to 8 after sowing of Ler and mutant plants onto vertically oriented plates. The asterisk indicates that tan1 air9 roots were significantly shorter than others (P < 0.01). F to I, Maximum projections of 10 0.2-µm Z-stacks showing expansion to the differentiation zone of propidium iodide-stained roots of Ler (F), tan1 (G), air9 (H), and tan1 air9 (I). J, Root cell file rotation (twisting) measurements. Each dot represents an angle measured from the transverse wall to the long axis of the root. Angles greater than 90° are left twisting and angles less than 90° are right twisting. The asterisk indicates a significant difference in the distribution of tan1 air9 cell file rotation compared with others (P < 0.01). Bars = 50 µm (A–D) and 200 µm (F–I).