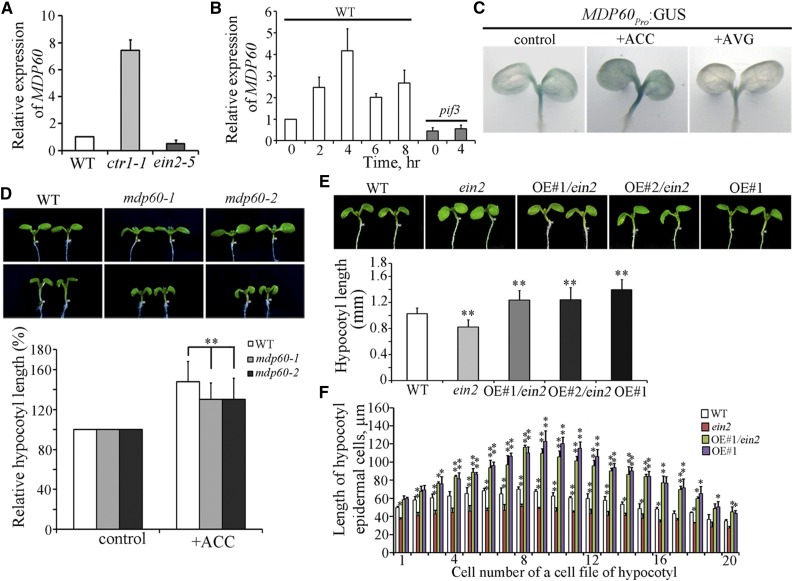
Figure 2.
Ethylene upregulates MDP60 expression to promote hypocotyl cell elongation. A, MDP60 expression was determined using quantitative real-time PCR with RNA purified from wild-type, ctr1-1, or ein2-5 5-d-old light-grown seedlings. Error bars represent ± sd (n = 3). B, Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of MDP60 RNA levels in 5-d-old wild-type and pif3 mutant seedlings treated with 10 μm ACC for the indicated times. UBQ11 was used as a reference gene. Error bars represent mean ± sd (n = 3). C, GUS staining of MDP60pro:GUS transgenic lines in the absence or presence of ACC and AVG. D, Wild-type and mdp60 mutant seedlings were grown on half-strength Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with or without ACC in the light for 7 d. The graph shows the relative hypocotyl length measured from at least 66 seedlings per sample grown on the medium supplemented with 0 and 10 μm ACC under light growth conditions. Three independent experiments were performed with similar results, each with three biological repeats. t test, **P < 0.01, error bars represent the mean ± se, n = 3. E, MDP60 transgenic mutant ein2-5 (OE#1/ein2 and OE#2/ein2) seedlings had much longer hypocotyls than wild-type seedlings but were similar in hypocotyl length to MDP60 transgenic wild-type (OE#1) seedlings when grown in the light for 7 d. The graph shows the average hypocotyl length measured from at least 41 seedlings per sample (**P < 0.01, t test). Error bars indicate the mean ± sd. F, Lengths of hypocotyl cells from wild-type, ein2-5, and MDP60 transgenic ein2-5 mutants (OE#1/ein2) and wild-type seedlings (OE#1) grown in the light for 7 d. t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Error bars represent mean ± sd.