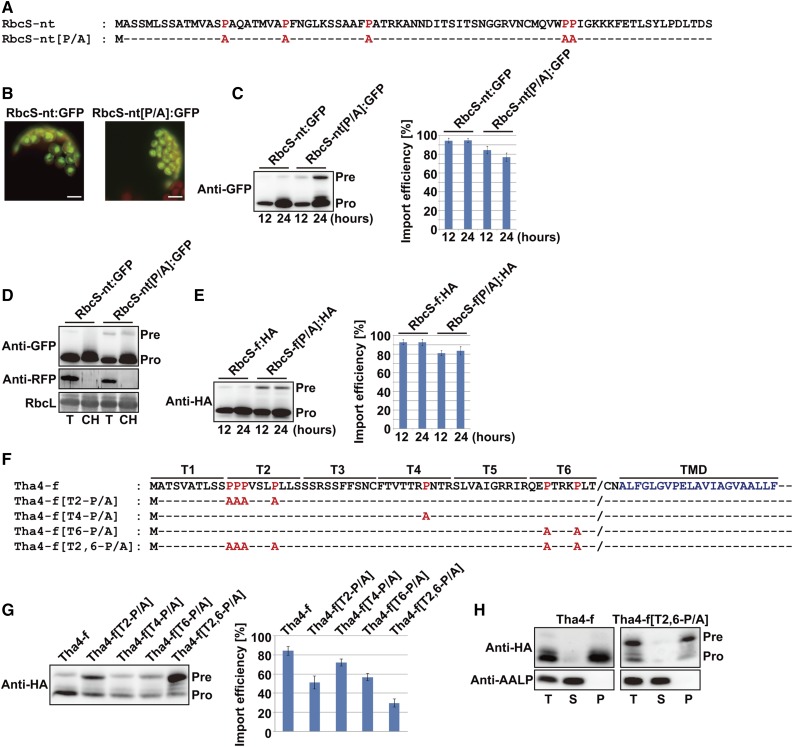
Figure 1.
Pro residues in TPs affect preprotein translocation into chloroplasts. A and F, Sequences of wild-type TPs and their P/A substitution mutants. P/A substitutions are indicated in red. B, Localization of reporter proteins. Protoplasts from Arabidopsis leaf tissues were transformed with the indicated constructs, and GFP patterns were observed 12 to 24 h after transformation. Green, red, and yellow signals represent GFP, chlorophyll autofluorescence, and the overlap between green and red signals, respectively. Scale bar = 20 μm. C, E, and G, Western-blot analysis of reporter proteins. Protein extracts from protoplasts were analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies. Import efficiency is defined as the percentage of the processed form divided by the total amount of expressed protein. The protein band intensity was measured using software installed on the LAS3000 imager (FUJI FILM). Data represent means (n = 3) with sd. Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form. D, Copurification of RbcS-nt[P/A]:GFP precursors with chloroplasts. Protoplasts were gently lysed 12 h after transformation, and chloroplasts were isolated using a Percoll gradient. Total and chloroplast fractions were analyzed by western blotting with anti-GFP and anti-RFP antibodies. RFP, cotransformed control for cytosolic proteins. Rubisco complex large subunit (RbcL) stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) was used as a loading control. T, total protein; CH, chloroplast fraction; Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form. H, Subcellular fractionation by ultracentrifugation. Fractions were analyzed by western blotting with anti-GFP antibody. Endogenous AALP was used as a control for soluble proteins. T, total protein; S, soluble fraction; P, pellet fraction; Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form.