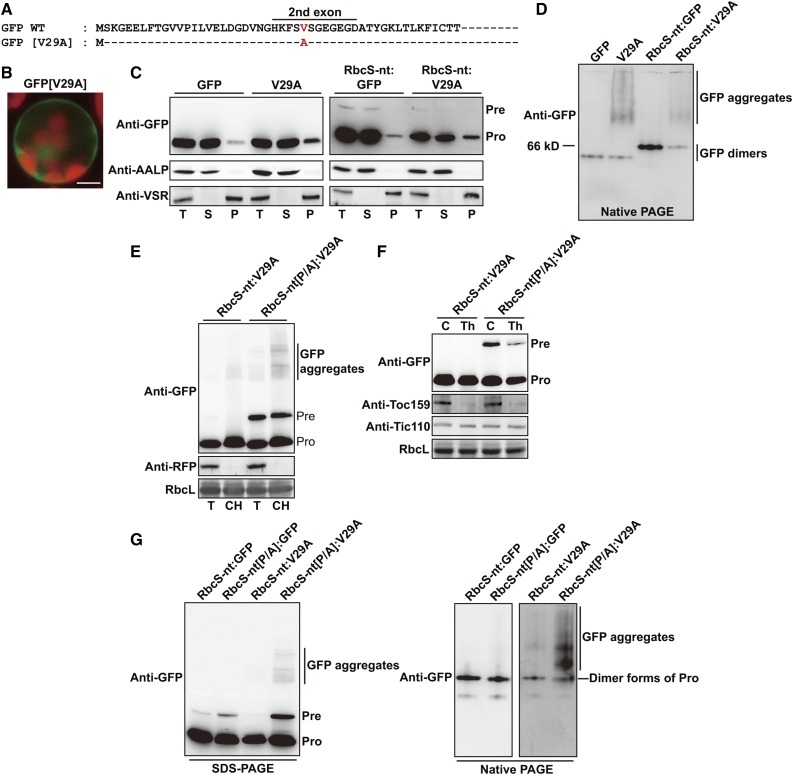
Figure 8.
Pro residues in TPs are crucial for efficient translocation of aggregation-prone preproteins through import channels. A, Partial sequences of wild-type GFP and GFP[V29A]. B, Localization of reporter proteins. Protoplasts were observed 12 h after transformation. Green, red, and yellow signals represent GFP, chlorophyll autofluorescence, and the overlap between green and red signals, respectively. Scale bar = 20 μm. C, Subcellular fractionation. Protein extracts were separated into soluble and pellet fractions by ultracentrifugation, and fractions were analyzed by western blotting with anti-GFP antibody. AALP and VSR were used as controls for the soluble and pellet fractions, respectively. T, total protein; S, soluble fraction; P, pellet fraction; Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form. D and G, Analysis of reporter proteins using SDS-PAGE and nondenaturing native PAGE. Total protein extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and nondenaturing native PAGE, followed by western blotting using anti-GFP antibody. Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form. E, Association of RbcS-nt[P/A]:GFP[V29A] preproteins with chloroplasts. Protoplasts were transformed with RbcS-nt[P/A]:GFP[V29A] together with RFP. Chloroplasts were isolated from protoplasts 12 h after transformation using a Percoll gradient. Total and chloroplast fractions were analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-RFP antibodies. RbcL was used as a loading control. T, total protein; CH, chloroplast fraction; Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form. F, Sensitivity of RbcS-nt[P/A]:GFP[V29A] preproteins to thermolysin. Gently lysed protoplast extracts were treated with thermolysin and then analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP, anti-Toc159, and anti-Tic110 antibodies. Pre, precursor form; Pro, processed form; T, total protein; CH, chloroplast fraction; RbcL, loading control.