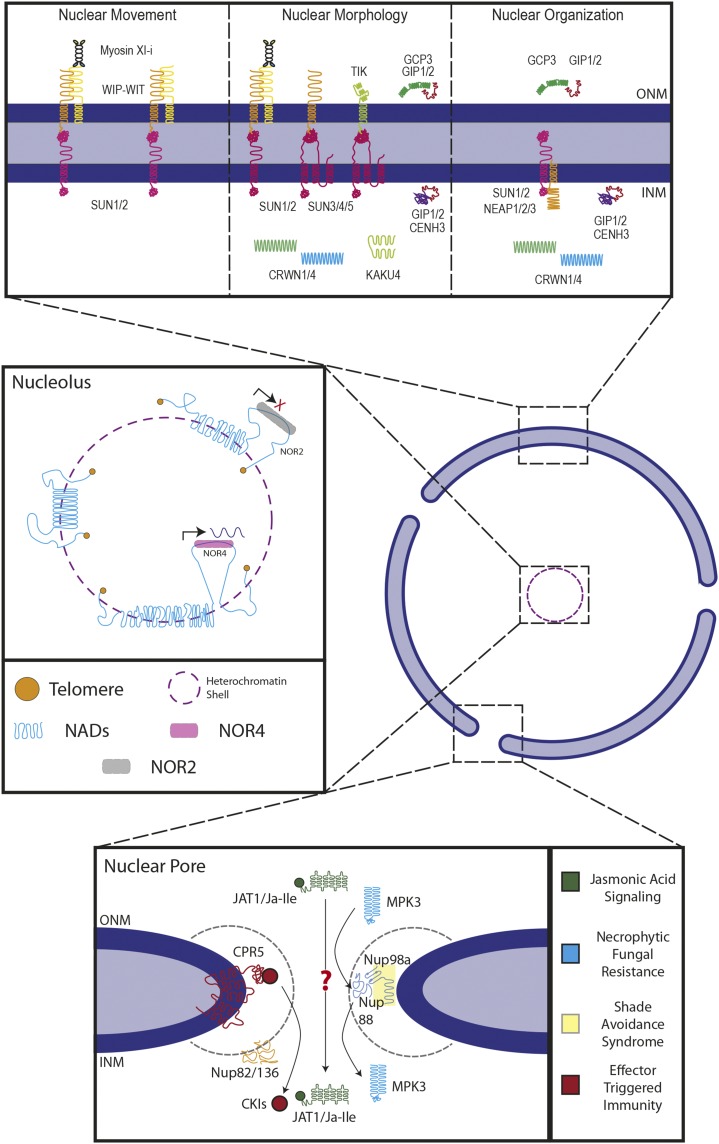
Figure 1.
Key elements involved in nuclear dynamics. Top box, Nuclear envelope proteins involved in nuclear dynamics. SUN-WIP-WIT complexes have been implicated in nuclear movement in pollen tubes. The SUN-WIP-WIT-Myosin XI-i LINC complex has been shown to be required for nuclear movement and nuclear positioning in root hairs. The SUN-WIP-WIT2-MyosinXI-i complex has also been shown to be required for nuclear shape determination in root hairs, as have the Mid-SUN domain proteins (SUN3/4/5). Mid-SUNs have been shown to interact with the KASH proteins WIPs and TIK. The plant lamin-like proteins CRWN1 and CRWN4 are required for nuclear shape determination and play a role in nuclear organization as well. KAKU4 interacts with CRWN1/4 and is additionally required for nuclear shape determination. The NE-associated proteins NEAP1–3 physically interact with SUN1/2 and are in some cell types required for nuclear shape determination. The NE-associated proteins GIP1/2 play a role in nuclear morphology, as well as nuclear organization, in concert with their interactors GCP3, in the cytoplasm, and CENH3, in the nucleoplasm. Middle box, The nucleolus is surrounded by a heterochromatic shell (purple dashes), which includes dense networks of chromatin known as nucleolus-associated chromatin domains (NADs, blue lines). Nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) contain rRNA genes, where NOR4 associates with the nucleolus and is actively expressed (pink shaded box; arrow depicting high transcriptional activity), while NOR2 is not associated with the nucleolus and has little transcriptional activity (gray shaded box; red X depicts low transcriptional activity). Telomeres (orange circles) are generally located within the nucleolus. Bottom box, Several nucleoporins are implicated in plant biotic and abiotic responses. Colors indicate association with a particular pathway, as marked on the right. Nups are drawn at predicted positions within the nuclear pore. Close association between Nups indicates confirmed protein-protein interaction. For details, see text.