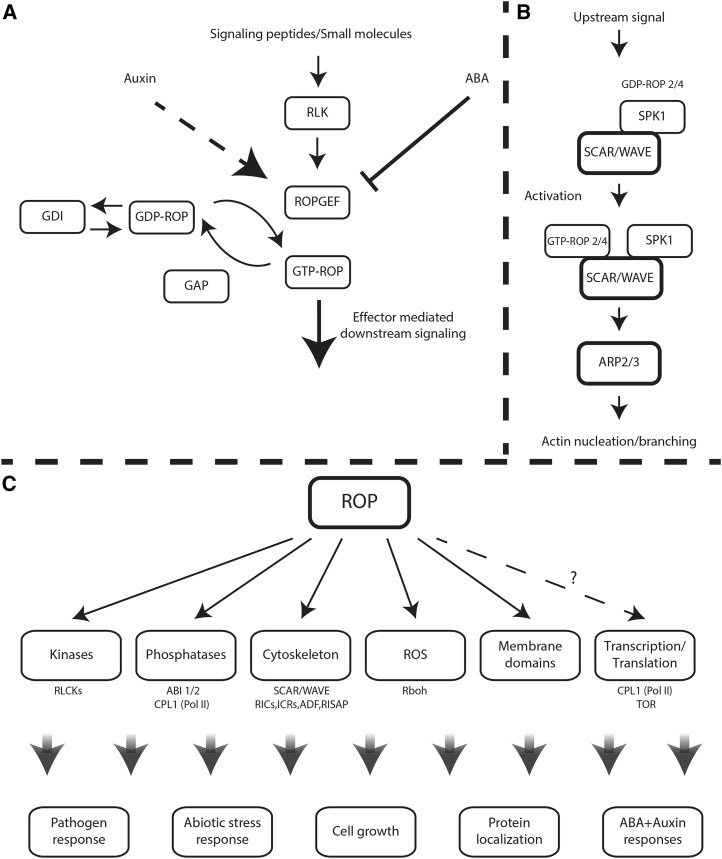
Figure 1.
ROP signaling pathways. A, ROP activation/deactivation cycles. ROPs cycle between a GTP-bound active state and a GDP-bound inactive state. Activation is regulated by ROP-specific GEFs, inactivation is enhanced by ROP-specific GAPs, and recycling of type I ROPs between the cytosol and the plasma membrane is facilitated by RhoGDIs. Some GEFs are activated by peptide-activated, plasma membrane-associated RLKs. ROPs also are up-regulated by auxin by an as yet unknown pathway (dashed arrow) and inactivated by ABA, which enhances the degradation of ROPGEFs. B, The Dock family GEF homolog SPK1 is associated with the WAVE complex. Upon activation, ROP-GTP interacts with the WAVE SRA1 subunit and possibly other subunits, resulting in WAVE activation. Activated WAVE activates actin nucleation/branching induced by Arp2/3. C, ROP downstream signaling. ROP regulated pathways and known effectors. The dashed arrow indicates uncertainty regarding the cellular targets of ROP. CPL1 is regulated by ROP signaling but does not interact physically with ROPs. TOR interacts weakly with GTP-bound ROP2 and more strongly with the GDP-bound form.