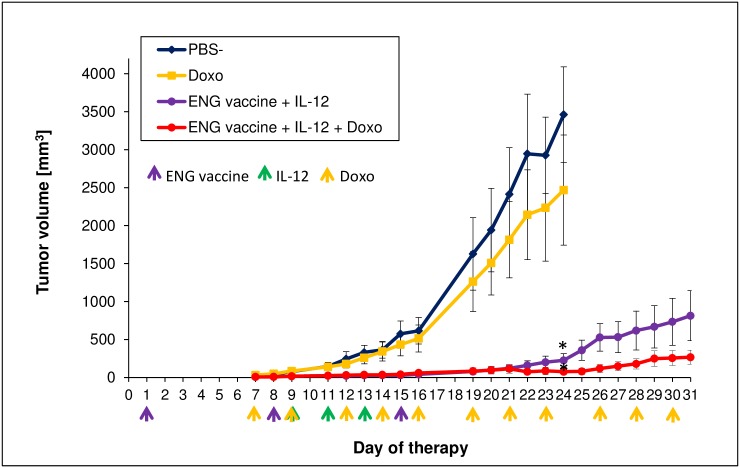
Fig 10. Inhibition of B16-F10 tumor growth in response to combination therapy involving endoglin-based DNA vaccine, IL-12 and chemotherapy.
One day after inoculating mice (n = 6–7) with B16-F10 cells, the animals were orally vaccinated (three times at one-week intervals). Additionally, on days 9, 11 and 13 following inoculation with cancer cells, IL-12 was injected directly into tumors (Materials and methods). Moreover, doxorubicin (Doxo) was delivered intraperitoneally at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg, 3 times/week. “Control” mice received PBS¯ only. The suboptimal doses of the cytotoxic agent doxorubicin inhibited the growth of tumors in mice treated with combined therapy, but only slightly inhibited the tumor growth in controls. * P<0.01, the ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s post hoc test.