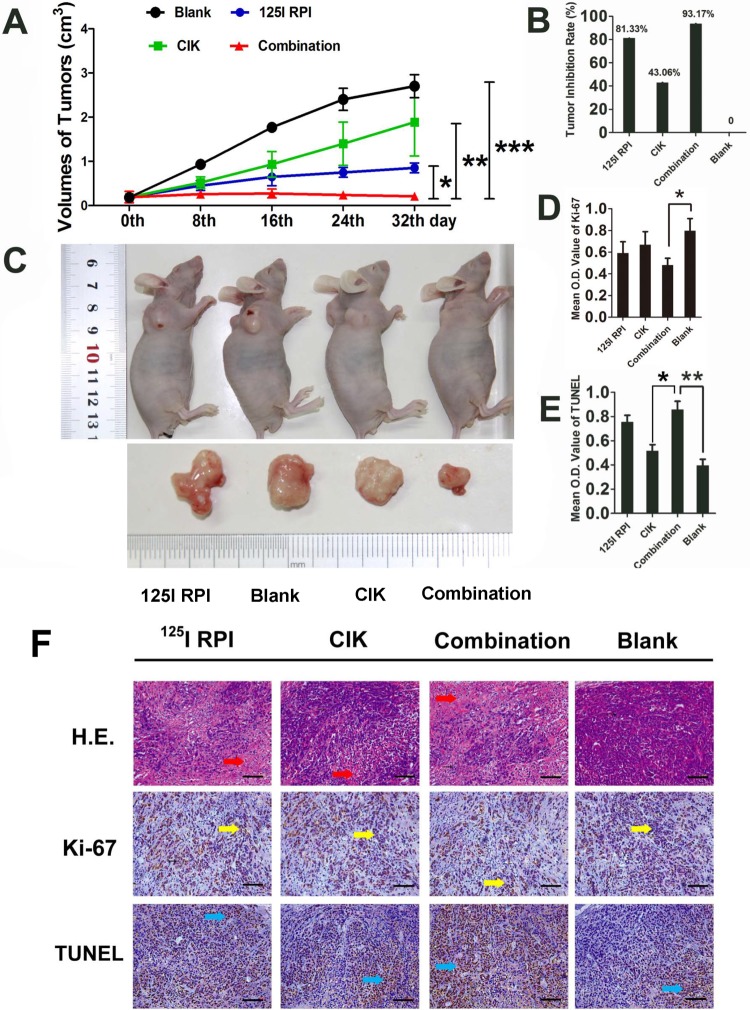
Figure 1.
Therapeutic effects of 125I RPI or/and CIK cells to HCC xenografts in BALB/c nude mice. A, B, and C, Thirty-two days after the initiation of treatment, the tumor volumes in the 125I RPI group and the CIK cell group were significantly smaller than those in control groups. The smallest tumor sizes were observed in the combination therapy group when compared to other groups (*P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001). The highest TIR was observed in the combination therapy group. D, E, and F, The images were taken randomly, not intentionally. Statistically significant differences were observed in the mean OD values of Ki-67 and TUNEL staining between the control group and treatment groups. The combination of 125I particle implantation and CIK cell therapy showed the highest inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis (*P < .001, F = 318.373; ***P < .001, F = 24.334, respectively). The only significant differences in TUNEL OD values between treatment groups were observed between the CIK cell therapy group and the combination therapy group (**P < .001, F = 207.491). CIK indicates cytokine-induced killer; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; OD, optical density; RPI, radioactive particle implantation; TIR, tumor inhibitory rate; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase(TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling.