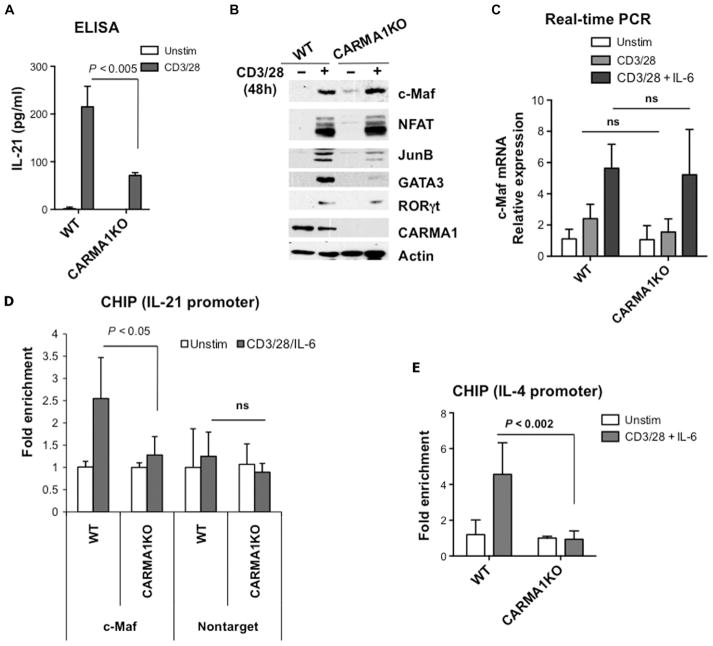
Fig. 1. CARMA1-deficient CD4+ T cells show decreased recruitment of c-Maf to the Il21 promoter and reduced production of IL-21.
(A) CD4+ splenocytes from wild-type (WT) and CARMA1-deficient (CARMA1KO) mice were stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3ε (2 μg/ml) and anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) antibodies for 48 hours. Secretion of IL-21 into the cell culture medium was determined by ELISA of triplicate cultures. Data are means ± SD. (B) TCR-induced expression of c-Maf does not require CARMA1. CD4+ T cells from the indicated mice were stimulated as described in (A). Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for c-Maf, GATA3, JunB, NFATc1, RORγt, actin, and CARMA1. Western blots are representative of two independent experiments. (C) CD4+ T cells from the indicated mice were activated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the presence or absence of IL-6 (20 ng/ml) for 18 hours. Total RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed, and quantitative PCR was performed with the SYBR Green PCR Master Mix. The amounts of c-Maf transcript were normalized to those of Gapdh, and the amounts of c-Maf mRNA in stimulated cells relative to those in unstimulated cells were calculated. The experiment was performed in triplicate, and data are means ± SD. (D and E) Defective recruitment of c-Maf to the Il4 and Il21 promoters in CARMA1KO T cells. CD4+ splenocytes from the indicated mice were activated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the presence of IL-6 for 18 hours, and then c-Maf–DNA complexes were precipitated with c-Maf antibody. Real-time PCR analysis for (D) the Il21 promoter and (E) the Il4 promoter was performed in triplicate, and results are means ± SD. Data are representative of two independent experiments. ns, not significant.