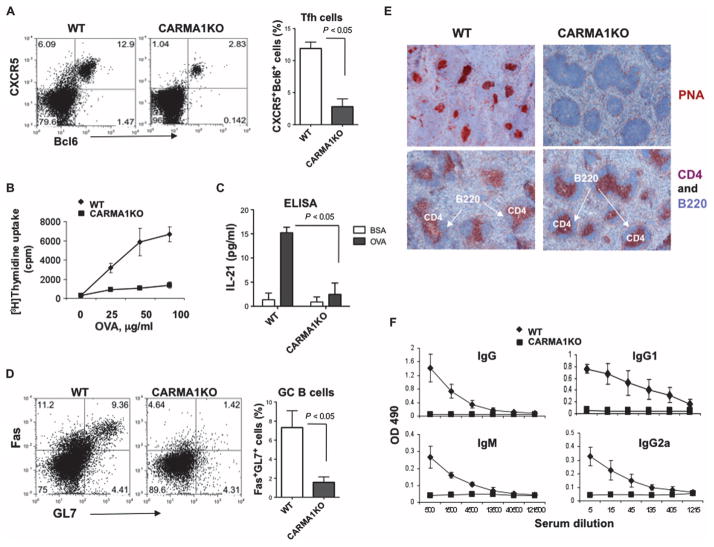
Fig. 5. CARMA1 is required for the generation of TFH cells and the formation of GCs after immunization of mice with OVA peptide.
(A) Immunized CARMA1-deficient mice generate reduced amounts of TFH cells. CARMA1KO mice and age-matched WT control mice (three mice per group) were immunized subcutaneously at the base of tail with OVA peptide emulsified in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA). Seven days after immunization, the mice were sacrificed and analyzed individually. TFH cells (CD4+CXCR5+Bcl6+ cells) were identified by flow cytometric analysis. Dot plots are from a representative experiment, and the histogram shows means ± SD from three mice of each genotype. (B) Splenocytes collected from each immunized mouse [from (A)] were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of OVA peptide for 48 hours. Cellular proliferation was then assayed by adding [3H]thymidine to the cultures for the last 8 hours. Data are means ± SD from three mice of each genotype. (C) Splenocytes from each of the immunized mice were restimulated with OVA peptide (100 μg/ml) for 72 hours, cell culture medium was collected, and the amounts of IL-21 produced were determined by ELISA. Data are means ± SD of triplicate cultures. (D) CARMA1 is required for the generation of GC B cells. CARMA1KO and WT control mice were immunized as described in (A), and splenocytes were isolated. GC B cells (B220+GL7+FasHigh) were determined by flow cytometry. Dot plots are from a single representative experiment, and the histogram shows means ± SD from three mice of each genotype. (E) Formation of GCs is reduced in immunized CARMA1KO mice. GCs in the spleens of the indicated mice immunized with OVA peptide were determined by immunohistochemical staining with anti-mouse PNA antibody (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin. T cells and B cells were identified by staining with anti-CD4 (red) and anti-B220 (blue) antibodies, respectively. Images are from one experiment and are representative of three independent experiments with consistent results. (F) Defective production of OVA-specific antibodies in CARMA1KO mice. Sera from the indicated immunized mice were subjected to serial dilutions, and the concentrations of OVA-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies were analyzed by ELISA and averaged for each group. Graphs show the means ± SD from three mice of each genotype.