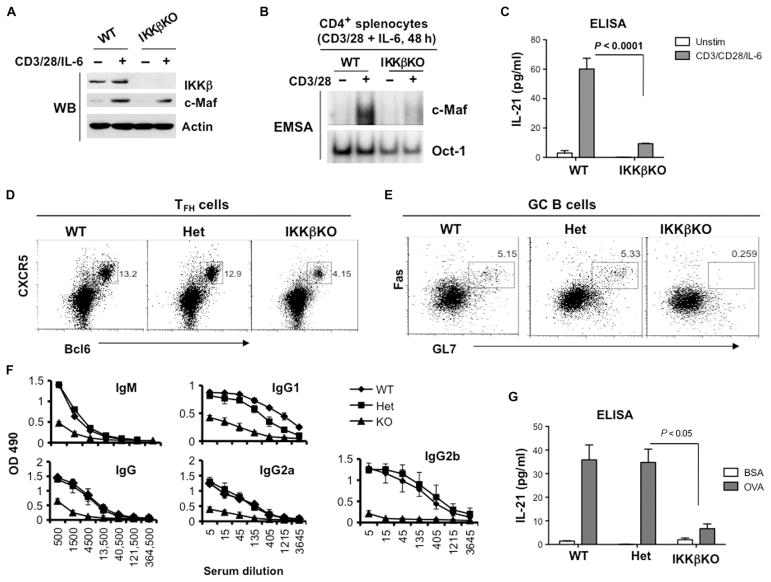
Fig. 6. Loss of IKKβ in CD4+ T cells impairs the activation of c-Maf and inhibits the development of TFH cells in vivo.
(A) The TCR-dependent increase in c-Maf abundance does not require IKKβ. CD4+ splenocytes from the indicated mice were stimulated with plate-bound antibodies against CD3 and CD28 (2 and 1 μg/ml, respectively) in the presence of IL-6 (20 ng/ml) for 48 hours. Whole-cell lysates were then analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins. Blots are representative of two experiments. (B) CD4+ splenocytes from the indicated mice were activated as described in (A), and nuclear extracts were analyzed by EMSA with 32P-labeled probes containing c-Maf– or Oct-1–binding sites. Data are representative of three experiments. (C) The amounts of IL-21 secreted by splenocytes from the indicated mice were determined by the analysis of culture media by ELISA. Data are means ± SD from triplicate cultures and are representative of three independent experiments. (D to G) WT, IKKβ heterozygous (Het), and IKKβ-deficient (IKKβKO) mice (two mice per group) were immunized subcutaneously at the base of tail with OVA peptide emulsified in CFA. Seven days after immunization, the mice were sacrificed and analyzed individually. (D and E) IKKβ is required for the generation of TFH cells and GC B cells. Splenocytes were isolated from the indicated immunized mice, and TFH cells (CD4+CXCR5+Bcl6+ cells) and GC B cells (B220+GL7+FasHigh) were determined by flow cytometry. Dot plots are from a single representative experiment. (F) Defective production of OVA-specific antibodies in IKKβKO mice. Sera from the indicated immunized mice were subjected to serial dilutions, and the concentrations of OVA-specific IgM and IgG antibodies were analyzed by ELISA. Data are means ± SD from each experimental group calculated from triplicate measurements. (G) Splenocytes from the indicated immunized mice were restimulated with OVA peptide (100 μg/ml) for 48 hours, and IL-21 production was determined by ELISA. Data are means ± SD of triplicate cultures.