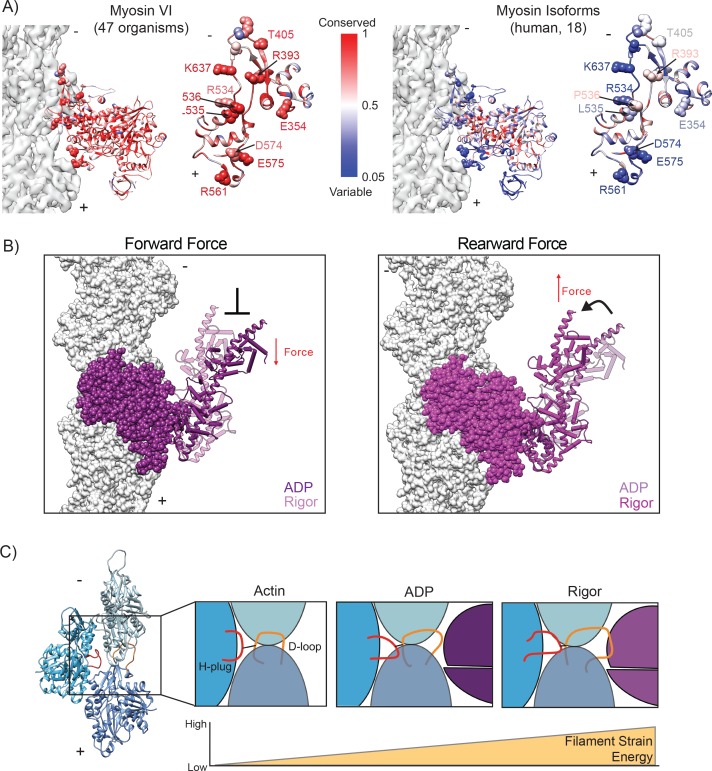
Figure 7. Conceptual models summarizing implications of the ADP to rigor transition.
(A) Conservation of myosin VI between 47 organisms (left, Source Data 1) and among 18 human myosin isoforms (right, Source Data 2). Left, full MD; Right, en face view of actin binding interface with space-filling representation of critical residues mediating actin interaction. Actin density is displayed in transparent grey for reference. (B) Schematic of potential effects of force on the ADP to rigor transition. Due to the displacement associated with the lever arm bend, a rearward load should favor ADP engagement and a forward load should disfavor it. The displayed superposition was generated as in Figure 5D. (C) Cartoon depicting increased actin strain during myosin force generation. The MD (magenta) - D-loop (orange) interaction facilitates remodeling of the H-plug (red).