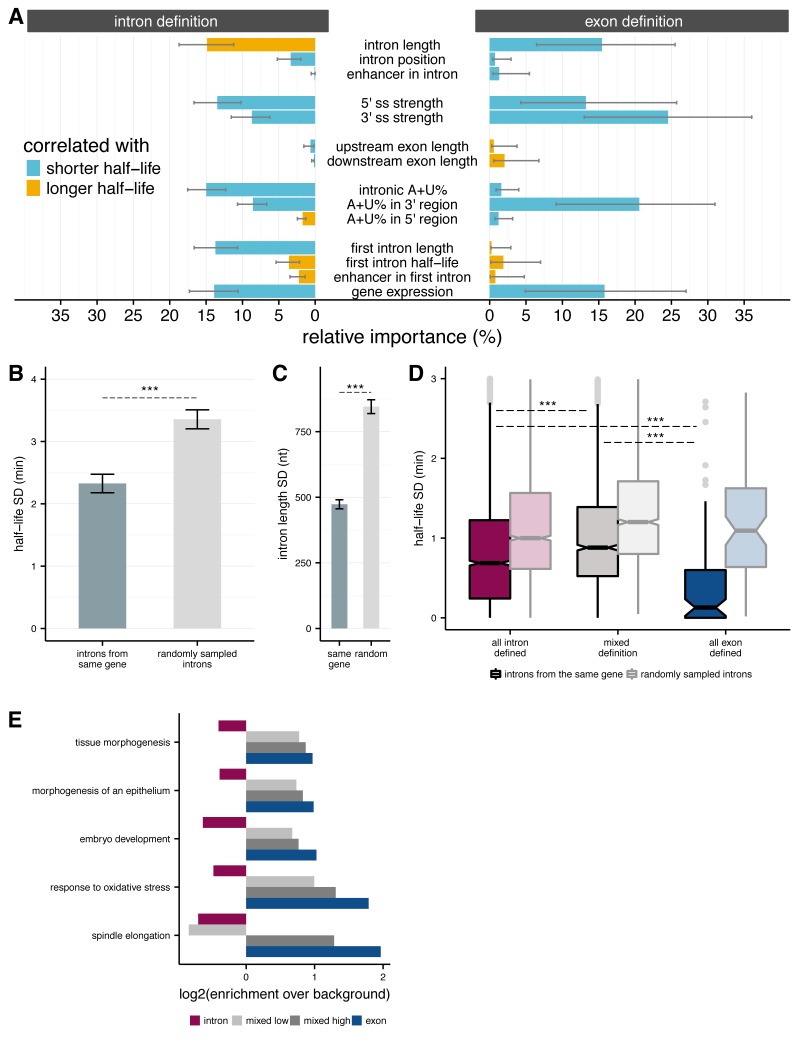
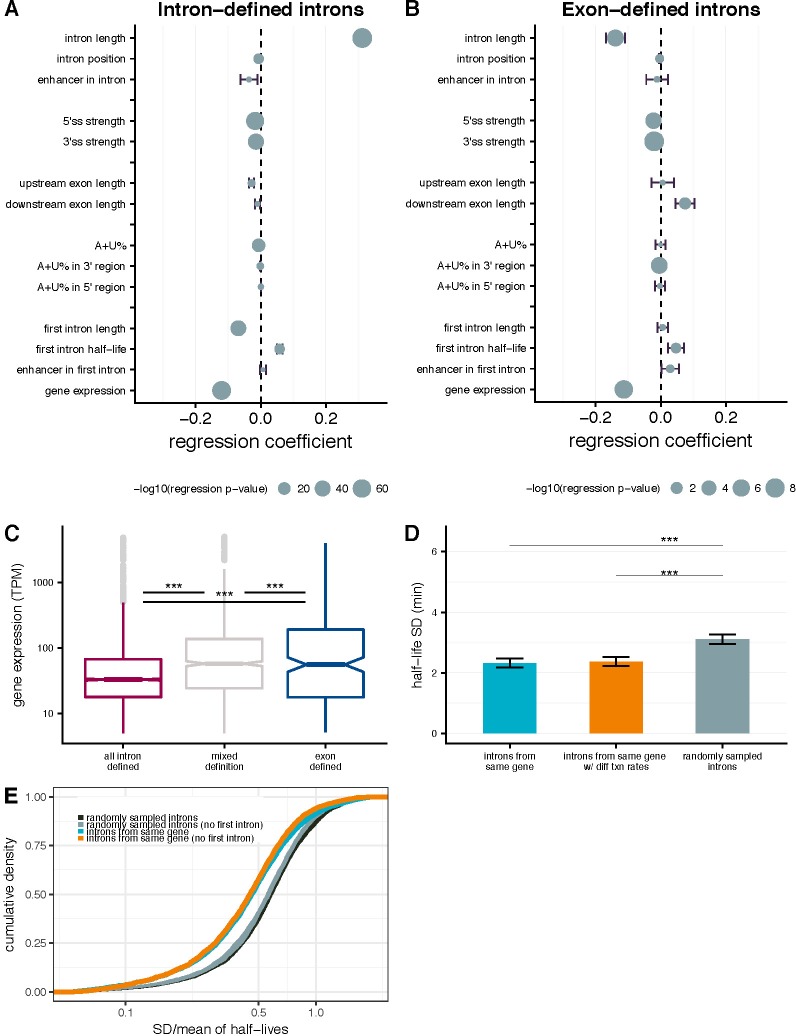
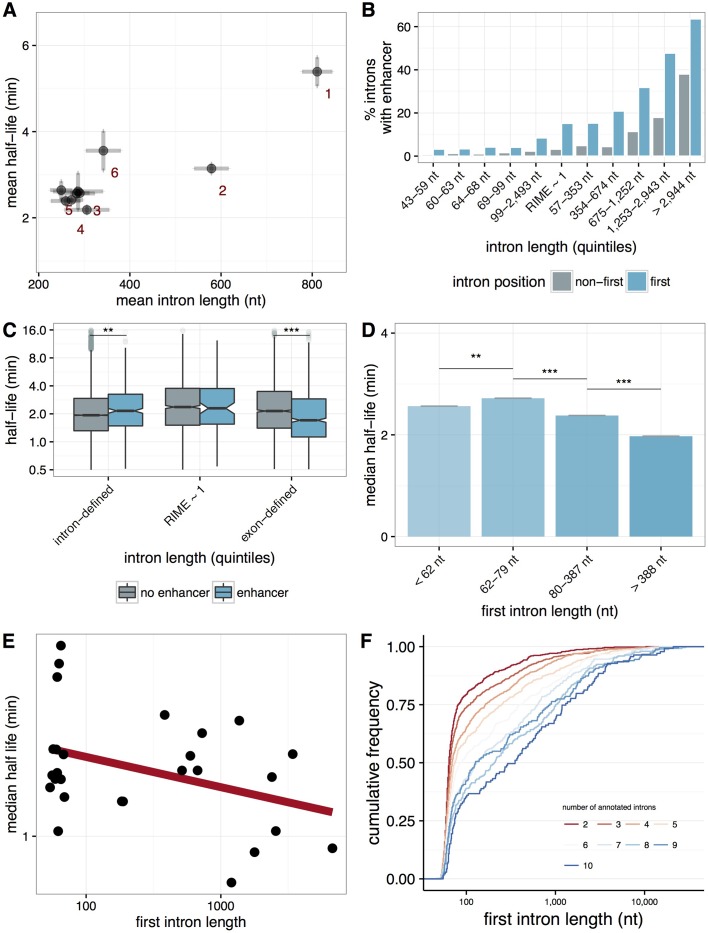
Figure 4. Splicing efficiency across introns within a gene.
(A) Relative importance of variables influencing variance in splicing half-lives in intron-defined (left) and exon-defined (right) introns, using a multiple linear-regression to account for variance in half-lives for non-first introns. (B) Mean variance of splicing half-lives across introns within a gene relative to randomly sampled introns (chosen to match the distribution of lengths within actual genes; error bars are ± standard error). (C) Average standard deviation of intron lengths across introns within a gene relative to randomly sampled introns (error bars are ± standard error). (D) Average standard deviation of splicing half-lives across introns within genes with mostly intron-defined introns (left), mostly exon-defined defined introns (right), and a mixture of definition classes (middle), relative to randomly sampled introns within each category of genes (lighter colors). (E) Enrichment of genes (x-axis; log2) within Gene Ontology categories that are significantly over-represented among exon-defined genes (y-axis) for classes of genes with increasing proportions of exon-defined genes: all intron-defined (pink), mixed-definition (grey), and exon-defined (blue).