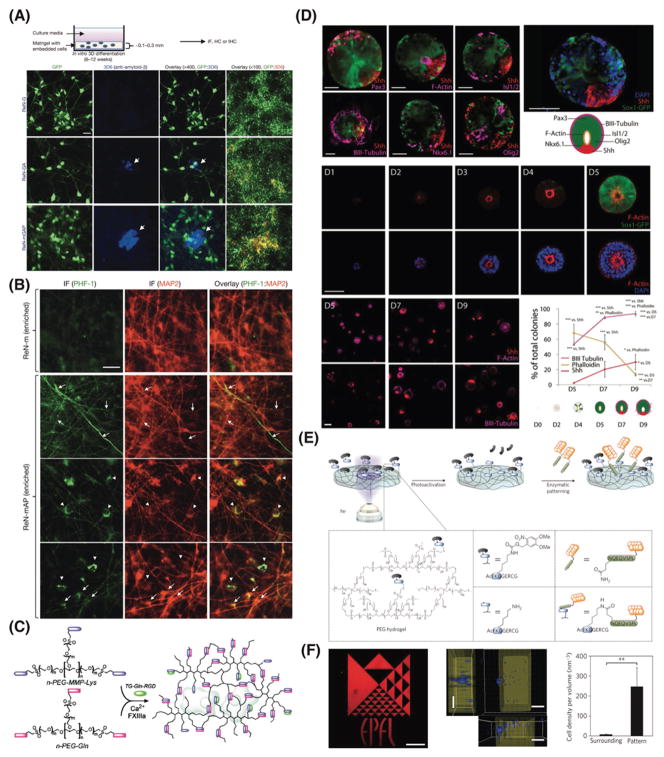
Figure 7.
Recapitulating the 3D native extracellular matrix using natural and synthetic matrices. A) 3D in vitro human neural cell culture model of AD using human neural progenitor cells embedded in Matrigel showing the two pathological hallmarks of AD, including extracellular aggregation of Aβ and (B) accumulation of intercellular hyperphosphorylated tau proteins. Reproduced with permission.[12] Copyright 2014, Nature Publishing Group. C) Enzymatically responsive multifunctional synthetic hydrogels using factor XIIIa for cross-linking two multi-arm PEG peptide conjugates in combination with coupling a cell adhesion peptide. Reproduced with permission.[198] Copyright 2007, American Chemical Society. D) Dorsal-ventral patterning and neural tube architecture in synthetic multi-arm PEG matrices to control early neural morphogenesis and to explore the role of ECM in the development of 3D neuroepithelial organoids. Cyst patterning shows key characteristics of neural tube architecture. Reproduced with permission.[201] Copyright 2016, National Academy of Sciences. E) Schematic representation of the concept of photo-responsive enzymatic peptide patterning of hydrogels, and (F) spatial patterning of hydrogels using ultraviolet light on a specific region within the hydrogel. Reproduced with permission.[204] Copyright 2013, Nature Publishing Group.