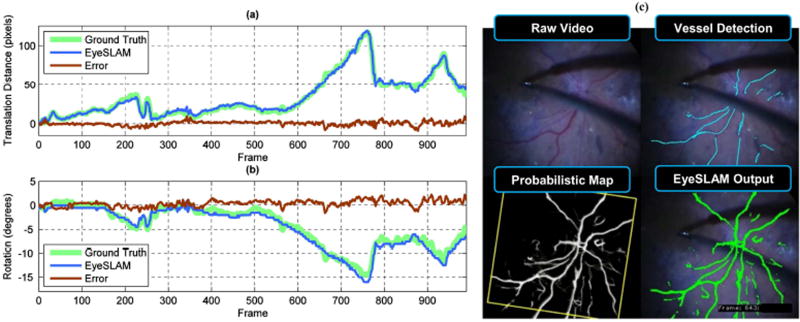
Fig. 4.
Localization accuracy and error compared to labeled video of human retina in vivo of a patient with retinopathy. (a) Translation component representing the L2 norm of X and Y (b) Rotation component (c) Sample output of raw video, vessel detection, map, and localized EyeSLAM output from frame 643. This system was able to perform vessel detection and localization in diseased eyes with retinal hemorrhages. Notice the accumulated evidence of seeing a vessel over many frames adds persistence of the mapped vessel structure through transient false negatives (no observed vessels because of tool occlusion). One failure mode is persistent occlusions will yield a repeated lack of vessel observations and remove vessels from the map once the probability decays too low. Loop closure global optimization would help with the small amount of angular drift seen in the latter part of the sequence.